BGP path attributes
Path attributes classification
BGP path attributes are a group of parameters encapsulated in the path attributes field of update messages. They give detailed route attributes information that can be used for route filtering and selection.
Path attributes fall into the following categories:
Well-known mandatory—Must be recognized by all BGP routers and be included in every Update message. Routing information errors occur without this attribute.
Well-known discretionary—Can be recognized by all BGP routers and optionally included in every Update message as needed.
Optional transitive—Transitive attribute between ASs. A BGP router not supporting this attribute can still receive routes with this attribute and advertise them to other peers.
Optional non-transitive—If a BGP router does not support this attribute, it will not advertise routes with this attribute.
The usage of each BGP path attribute is described in the following table.
Table 7: Usage of BGP path attributes
Name | Category |
|---|---|
ORIGIN | Well-known mandatory |
AS_PATH | Well-known mandatory |
NEXT_HOP | Well-known mandatory |
LOCAL_PREF | Well-known discretionary |
ATOMIC_AGGREGATE | Well-known discretionary |
AGGREGATOR | Optional transitive |
COMMUNITY | Optional transitive |
MULTI_EXIT_DISC (MED) | Optional non-transitive |
ORIGINATOR_ID | Optional non-transitive |
CLUSTER_LIST | Optional non-transitive |
Usage of BGP path attributes
ORIGIN
ORIGIN is a well-known mandatory attribute that defines the origin of routing information (how a route became a BGP route). This attribute has the following types:
IGP—Has the highest priority. Routes added to the BGP routing table using the network command have the IGP attribute.
EGP—Has the second highest priority. Routes obtained via EGP have the EGP attribute.
INCOMPLETE—Has the lowest priority. The source of routes with this attribute is unknown, which does not mean such routes are unreachable. The routes redistributed from other routing protocols have the INCOMPLETE attribute.
AS_PATH
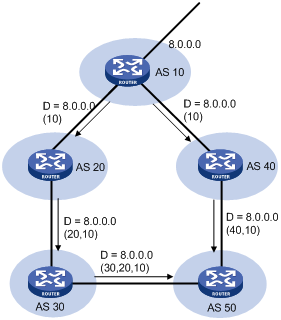
AS_PATH is a well-known mandatory attribute. This attribute identifies the autonomous systems through which routing information carried in this Update message has passed. When a route is advertised from the local AS to another AS, each passed AS number is added into the AS_PATH attribute, so the receiver can determine ASs to route the message back. The number of the AS closest to the receiver’s AS is leftmost, as shown in Figure 76:
Figure 76: AS_PATH attribute
Generally, a BGP router does not receive routes containing the local AS number to avoid routing loops.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: The current implementation supports using the peer allow-as-loop command to receive routes containing the local AS number in order to meet special requirements. | |
Use the AS_PATH attribute for route selection and filtering. BGP gives priority to the route with the shortest AS_PATH length, if other factors are the same. As shown in Figure 76, the BGP router in AS 50 gives priority to the route passing AS 40 for sending data to the destination 8.0.0.0.
In some applications, you can apply a routing policy to control BGP route selection by modifying the AS_PATH length.
By configuring an AS path filtering list, you can filter routes based on AS numbers contained in the AS_PATH attribute.
NEXT_HOP
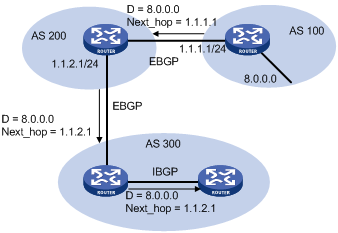
Different from IGP, the NEXT_HOP attribute may not be the IP address of a directly connected router. It involves the following types of values, as shown in Figure 77.
When advertising a self-originated route to an EBGP peer, a BGP speaker sets the NEXT_HOP for the route to the address of its sending interface.
When sending a received route to an EBGP peer, a BGP speaker sets the NEXT_HOP for the route to the address of the sending interface.
When sending a route received from an EBGP peer to an IBGP peer, a BGP speaker does not modify the NEXT_HOP attribute. If load-balancing is configured, the NEXT_HOP attribute of the equal-cost routes is modified. For load-balancing information, see "BGP route selection."
Figure 77: NEXT_HOP attribute
MED (MULTI_EXIT_DISC)
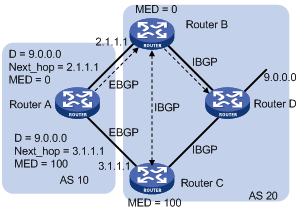
The MED attribute is exchanged between two neighboring ASs, each of which does not advertise the attribute to any other AS.
Similar to metrics used by IGP, MED is used to determine the best route for traffic going into an AS. When a BGP router obtains multiple routes to the same destination, but with different next hops, it considers the route with the smallest MED value the best route given that other conditions are the same. As shown in Figure 78, traffic from AS 10 to AS 20 travels through Router B that is selected according to MED.
Figure 78: MED attribute
In general, BGP compares MEDs of routes received from the same AS only.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: The current implementation supports using the compare-different-as-med command to force BGP to compare MED values of routes received from different ASs. | |
LOCAL_PREF
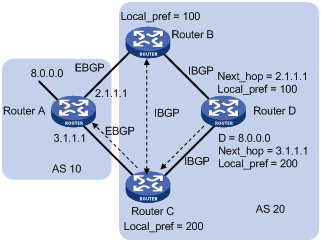
The LOCAL_PREF attribute is exchanged between IBGP peers only; therefore, it is not advertised to any other AS. It indicates the priority of a BGP router.
LOCAL_PREF is used to determine the best route for traffic leaving the local AS. When a BGP router obtains from several IBGP peers multiple routes to the same destination, but with different next hops, it considers the route with the highest LOCAL_PREF value as the best route. As shown in Figure 79, traffic from AS 20 to AS 10 travels through Router C that is selected according to LOCAL_PREF.
Figure 79: LOCAL_PREF attribute
COMMUNITY
The COMMUNITY attribute is a group of specific data. A route can carry one or more COMMUNITY attribute values (each of which is represented by a four-byte integer). The receiving router processes the route (for example, determining whether to advertise the route and the scope for advertising the route) based on the COMMUNITY attribute values. This simplifies routing policy usage and facilitates management and maintenance. Well-known community attributes are as follows:
INTERNET—By default, all routes belong to the Internet community. Routes with this attribute can be advertised to all BGP peers.
NO_EXPORT—After received, routes with this attribute cannot be advertised out the local AS or out the local confederation, but can be advertised to other sub-ASs in the confederation. For confederation information, see "Settlements for problems in large scale BGP networks."
NO_ADVERTISE—After received, routes with this attribute cannot be advertised to other BGP peers.
NO_EXPORT_SUBCONFED—After received, routes with this attribute cannot be advertised out the local AS or other ASs in the local confederation.