BGP messages formats
Header
BGP has the following types of messages:
Open
Update
Notification
Keepalive
Route-refresh
They have the same header.
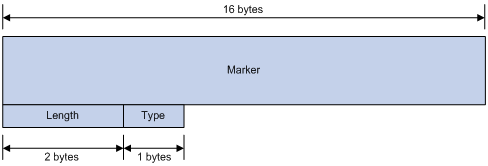
Figure 71: BGP message header
Marker—The 16-byte field is used to delimit BGP messages. The Marker must be all ones.
Length—The two-byte unsigned integer indicates the total length of the message.
Type—This one-byte unsigned integer indicates the type code of the message. The following type codes are defined: 1–Open, 2-Update, 3-Notification, 4–Keepalive, and 5–Route-refresh. The former four listed codes are defined in RFC 1771, and the last listed code is defined in RFC 2918.
Open
After a TCP connection is established, the first message sent by each side is an open message for peer relationship establishment.
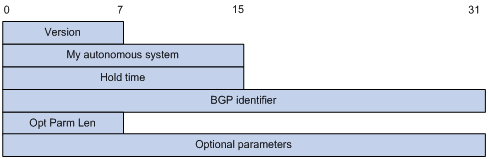
Figure 72: BGP open message format
Major fields of the BGP open message are as follows:
Version—This one-byte unsigned integer indicates the protocol version number. The current BGP version is 4.
My autonomous system—This two-byte unsigned integer indicates the autonomous system number of the sender.
Hold time—When establishing a peer relationship, two parties negotiate an identical hold time. If no Keepalive or Update is received from a peer within the hold time, the BGP connection is considered down.
BGP identifier—An IP address that identifies the BGP router.
Opt Parm Len (Optional Parameters Length)—Length of optional parameters, which is set to 0 if no optional parameter is available.
Optional parameters—Used for multiprotocol extensions and other functions.
Update
The update messages are used to exchange routing information between peers. It can advertise feasible routes or remove multiple unfeasible routes.
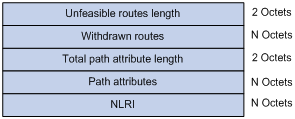
Figure 73: BGP update message format
Each update message can advertise a group of feasible routes with identical attributes, and the routes are contained in the network layer reachability information (NLRI) field. The path attributes field carries the attributes of these routes. Each update message can also carry multiple withdrawn routes in the withdrawn routes field.
Major fields of the BGP update message are as follows:
Unfeasible routes length—The total length of the withdrawn routes field in bytes. A value of 0 indicates no route is withdrawn from service, nor is the withdrawn routes field present in this update message.
Withdrawn routes—This is a variable length field that contains a list of withdrawn IP prefixes.
Total path attribute length—Total length of the path attributes field in bytes. A value of 0 indicates that no NLRI field is present in this update message.
Path attributes—List of path attributes related to NLRI. Each path attribute is a triple <attribute type, attribute length, attribute value> of variable length. BGP uses these attributes to avoid routing loops, and perform routing and protocol extensions.
NLRI—Each feasible route is represented as <length, prefix>.
Notification
A notification message is sent when an error is detected. The BGP connection is closed immediately after sending it.
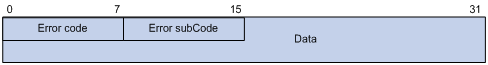
Figure 74: BGP notification message format
Major fields of the BGP notification message are as follows:
Error code—Type of notification.
Error subcode—Specific information about the nature of the reported error.
Data—Used to diagnose the reason for the notification. The contents of the data field depend on the error code and error subcode. Erroneous data can be recorded in the data field. The data field length is variable.
Keepalive
Keepalive messages are sent between peers to maintain connectivity. Its format contains only the message header.
Route-refresh
A route-refresh message is sent to a peer to request the specified address family routing information.
Figure 75: BGP route-refresh message format
AFI—Address family identifier.
Res—Reserved; set to 0.
SAFI—Subsequent address family identifier.