POS communication modes
POS applications on the router correspond to services on the FEPs. A POS application communicates with a FEP either through a TCP connection or a flow connection. Figure 18 illustrates these two connection modes.
TCP mode—The POS application communicates with the FEP through a TCP connection. The application can be identified by the IP address and port number of the FEP. Different applications correspond to services with the same IP address and different port numbers, or services with different IP addresses. In this mode, applications can be classified into normal connection applications and temporary connection applications. A normal connection application maintains only one TCP connection to the FEP, while a temporary connection application employs multiple TCP connections to the FEP.
Flow mode—The POS application is connected to the FEP through an asynchronous interface. The application is identified by the asynchronous interface. Each asynchronous interface corresponds to one application.
Figure 17: Network diagram of POS application connections
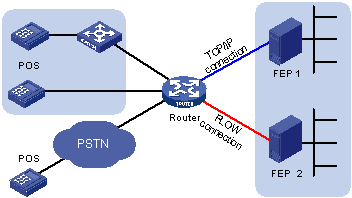
Upon receiving a packet from a POS terminal, the router encapsulates the packet according to the communication mode of the corresponding POS application, and sends the resulting packet to the FEP.