For information about virtual links, see Configuring an ABR to use a virtual link to the backbone.
Syntax:
Used on a pair of ABRs at opposite ends of a virtual link in the same area to configure the virtual link connection.
Example
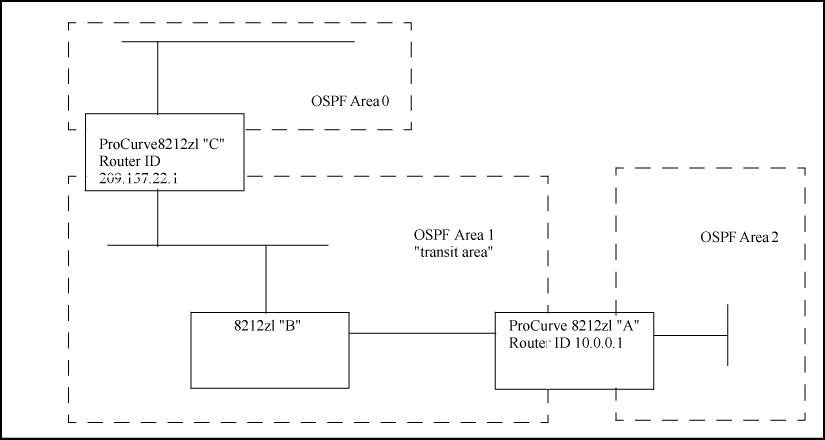
Defining OSPF virtual links within a network shows an OSPF ABR, routing switch "A" that lacks a direct connection to the backbone area (area 0.) To provide backbone access to routing switch "A," you can add a virtual link between routing switch "A" and routing switch "C," using area 1 as a transit area.
To configure the virtual link, define it on the routers that are at each end of the link. No configuration for the virtual link is required on the other routers on the path through the transit area (such as routing switch "B" in this example.)
To configure the virtual link on routing switch "A," enter the following command specifying the area 1 interface on routing switch "C":
HP Switch(ospf)# area 1 virtual-link 209.157.22.1
To configure the virtual link on routing switch "C," enter the following command specifying the area 1 interface on routing switch "A":
HP Switch(ospf)# area 1 virtual-link 10.0.0.1
For descriptions of virtual link interface parameters you can either use in their default settings or reconfigure as needed, see Changing the dead interval on a virtual link.
For more information, see Adjusting virtual link performance by changing the interface settings.
Syntax:
Used in the router OSPF context on both ABRs in a virtual link to change the number of seconds that a neighbor router waits for a hello packet from the specified interface before declaring the interface "down." This should be some multiple of the hello interval. The
dead-intervalsetting must be the same on both ABRs on a given virtual link.
Specifies the OSPF area in which both ABRs in a given virtual link operate. In this use, the area ID is sometimes termed "transit area ID."
This value must be the same for both ABRs in the virtual link.
For an ABR in a given virtual link, this is the IP address used to create the link on that ABR.
This IP address matches the IP address of the interface on the opposite end of the virtual link. See the description of
in the syntax description under Configuring a virtual link.ip-addressUse
show ip ospf virtual-linkto view the current setting.ip-address
Syntax:
Used in the router OSPF context on both ABRs in a virtual link to indicate the length of time between the transmission of hello packets between the ABRs on opposite ends of the virtual link.
The hello-interval setting must be the same on both ABRs on a given virtual link.
Default: 10 seconds; range: 1–65535 seconds
Specifies the OSPF area in which both ABRs in a given virtual link operate. In this use, the area ID is sometimes termed "transit area ID."
This value must be the same for both ABRs in the virtual link.
For an ABR in a given virtual link, this is the IP address used to create the link on that ABR. (This IP address matches the IP address of the interface on the opposite end of the virtual link. See the description of
in the syntax description under Configuring a virtual link.)ip-addressUse
show ip ospf virtual-linkto view the current setting.ip-address
Syntax:
Used in the router OSPF context on both ABRs in a virtual link to change the number of seconds between LSA retransmissions on the virtual link.
The retransmit-interval setting must be the same on both ABRs on a given virtual link. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets.
Specifies the OSPF area in which both ABRs in a given virtual link operate. In this use, the area ID is sometimes termed "transit area ID." This value must be the same for both ABRs in the virtual link.
For an ABR in a given virtual link, this is the IP address used to create the link on that ABR. (This IP address matches the IP address of the interface on the opposite end of the virtual link. See the description of
in the syntax description under Configuring a virtual link.)ip-addressUse
show ip ospf virtual-linkto view the current setting.ip-address
Syntax:
Used in the router OSPF context on both ABRs in a virtual link to change the estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet over a virtual link. The
transit-delaysetting must be the same on both ABRs on a given virtual link.
Specifies the OSPF area in which both ABRs in a given virtual link operate. In this use, the area ID is sometimes termed "transit area ID." This value must be the same for both ABRs in the virtual link.
For an ABR in a given virtual link, this is the IP address used to create the link on that ABR. (This IP address matches the IP address of the interface on the opposite end of the virtual link. See the description of
ip-addressin the syntax description under Configuring a virtual link.)Use
show ip ospf virtual-linkto view the current setting.ip-addressDefault: 1 second; range: 1–3600 seconds
Example
To change the hello-interval on the virtual link configured for the network in Defining OSPF virtual links within a network to 60 seconds:
On routing switch "A" (IP address 10.0.0.1) you would use the following command to reconfigure the current hello-interval to 60 seconds:
HP Switch(ospf)# area 1 virtual-link 209.157.22.1 hello-interval 60On routing switch "C" (IP address 209.157.22.1) you would use the following command to reconfigure the current hello-interval to 60 seconds
HP Switch(ospf)# area 1 virtual-link 10.0.0.1 hello-interval 60