Option 82 is called the relay agent information option and is inserted by the DHCP relay agent when forwarding client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server. Servers recognizing the relay agent information option may use the information to implement IP address or other parameter assignment policies. The DHCP server echoes the option back verbatim to the relay agent in server-to-client replies, and the relay agent strips the option before forwarding the reply to the client.
The relay agent information option is organized as a single DHCP option that contains one or more suboptions that convey information known by the relay agent. The initial suboptions are defined for a relay agent that is co-located in a public circuit access unit. These include a circuit ID for the incoming circuit and a remote ID that provides a trusted identifier for the remote high-speed modem.
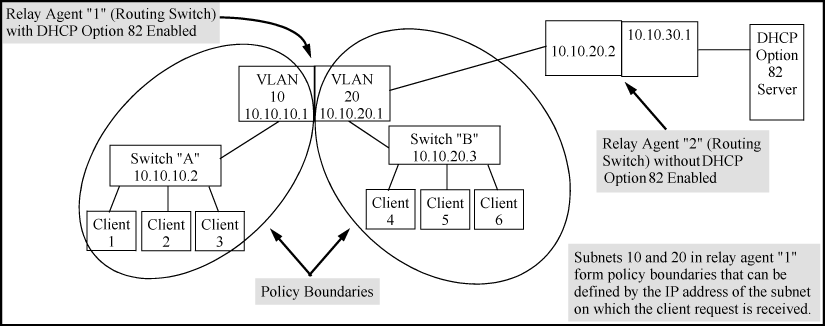
The routing switch can operate as a DHCP relay agent to enable communication between a client and a DHCP server on a different subnet. Without Option 82, DHCP operation modifies client IP address request packets to the extent needed to forward the packets to a DHCP server. Option 82 enhances this operation by enabling the routing switch to append an Option 82 field to such client requests. This field includes two suboptions for identifying the routing switch (by MAC address or IP address) and the routing switch port the client is using to access the network. A DHCP server with Option 82 capability can read the appended field and use this data as criteria for selecting the IP addressing it will return to the client through the usual DHCP server response packet. This operation provides several advantages over DHCP without Option 82:
-
An Option 82 DHCP server can use a relay agent's identity and client source port information to administer IP addressing policies based on client and relay agent location within the network, regardless of whether the relay agent is the client's primary relay agent or a secondary agent.
-
A routing switch operating as a primary Option 82 relay agent for DHCP clients requesting an IP address can enhance network access protection by blocking attempts to use an invalid Option 82 field to imitate an authorized client, or by blocking attempts to use response packets with missing or invalid Option 82 suboptions to imitate valid response packets from an authorized DHCP server.
-
An Option 82 relay agent can also eliminate unnecessary broadcast traffic by forwarding an Option 82 DHCP server response only to the port on which the requesting client is connected, instead of broadcasting the DHCP response to all ports on the VLAN.
It is not necessary for all relay agents on the path between a DHCP client and the server to support Option 82, and a relay agent without Option 82 should forward DHCP packets regardless of whether they include Option 82 fields. However, Option 82 relay agents should be positioned at the DHCP policy boundaries in a network to provide maximum support and security for the IP addressing policies configured in the server.
For more information, see the documentation provided with the server application.
To apply DHCP Option 82, the routing switch must operate in conjunction with a server that supports Option 82. (DHCP servers that do not support Option 82 typically ignore Option 82 fields.) Also, the routing switch applies Option 82 functionality only to client request packets being routed to a DHCP server. DHCP relay with Option 82 does not apply to switched (non-routed) client requests.
For information on configuring policies on a server running DHCP Option 82, see the documentation provided for that application.
DHCP Option 82 operation is configured at the global config level and requires the following:
-
IP routing enabled on the switch
-
DHCP-relay option 82 enabled (global command level)
-
Routing switch access to an Option 82 DHCP server on a different subnet than the clients requesting DHCP Option 82 support
-
One IP helper address configured on each VLAN supporting DHCP clients
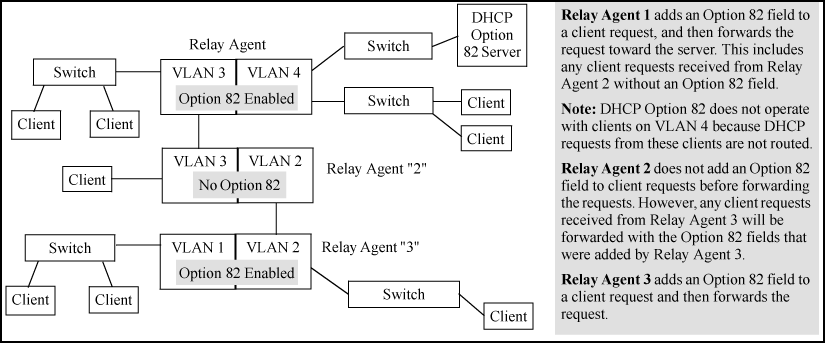
Typically, the first (primary) Option 82 relay agent to receive a client's DHCP request packet appends an Option 82 field to the packet and forwards it toward the DHCP server identified by the IP helper address configured on the VLAN in which the client packet was received. Other, upstream relay agents used to forward the packet may append their own Option 82 fields, replace the Option 82 fields they find in the packet, forward the packet without adding another field, or drop the packet. (Intermediate next-hop routing switches without Option 82 capability can be used to forward—route—client request packets with Option 82 fields.) Response packets from an Option 82 server are routed back to the primary relay agent (routing switch) and include an IP addressing assignment for the requesting client and an exact copy of the Option 82 data the server received with the client request. The relay agent strips off the Option 82 data and forwards the response packet out the port indicated in the response as the Circuit ID (client access port.) Under certain validation conditions described later in this section, a relay agent detecting invalid Option 82 data in a response packet may drop the packet.
The remote ID and circuit ID subfields comprise the Option 82 field a relay agent appends to client requests. A DHCP server configured to apply a different IP addressing policy to different areas of a network uses the values in these subfields to determine which DHCP policy to apply to a given client request.
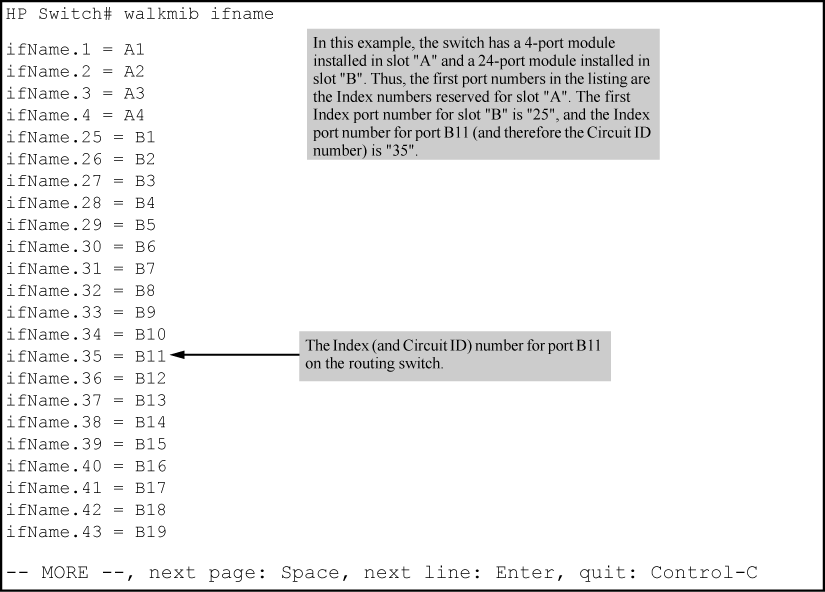
Using walkmib to determine the circuit ID for a port on an HP chassis
For example, the circuit ID for port B11 on an HP switch is "35”, see Using walkmib to determine the circuit ID for a port on an HP chassis, below.
For example, suppose you want port 10 on a given relay agent to support no more than five DHCP clients simultaneously. You can configure the server to allow only five IP addressing assignments at any one time for the circuit ID (port) and remote ID (MAC address) corresponding to port 10 on the selected relay agent.
Similarly, if you want to define specific ranges of addresses for clients on different ports in the same VLAN, you can configure the server with the range of IP addresses allowed for each circuit ID (port) associated with the remote ID (IP address) for the selected VLAN.
DHCP Option 82 on HP switches offers four forwarding policies, with an optional validation of server responses for three of the policy types (append, replace, or drop.)
Configuration options for managing DHCP client request packets:
| Option 82 configuration | DHCP client request packet inbound to the routing switch | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Packet has no Option 82 field | Packet includes an Option 82 field | |||||||
Append |
Append an Option 82 field | Append allows the most detail in defining DHCP policy boundaries. For example, where the path from a client to the DHCP Option 82 server includes multiple relay agents with Option 82 capability, each relay agent can define a DHCP policy boundary and append its own Option 82 field to the client request packet. The server can then determine in detail the agent hops the packet took, and can be configured with a policy appropriate for any policy boundary on the path.
|
||||||
Keep |
Append an Option 82 field | If the relay agent receives a client request that already has one or more Option 82 fields, keep causes the relay agent to retain such fields and forward the request without adding another Option 82 field. But if the incoming client request does not already have any Option 82 fields, the relay agent appends an Option 82 field before forwarding the request. Some applications for keep include:
This policy does not include the |
||||||
Replace |
Append an Option 82 field | Replace replaces any existing Option 82 fields from downstream relay agents (and/or the originating client) with an Option 82 field for the current relay agent. Some applications for replace include:
|
||||||
Drop |
Append an Option 82 field | Drop causes the routing switch to drop an inbound client request with an Option 82 field already appended. If no Option 82 fields are present, drop causes the routing switch to add an Option 82 field and forward the request. As a general guideline, configure drop on relay agents at the edge of a network, where an inbound client request with an appended Option 82 field may be unauthorized, a security risk, or for some other reason, should not be allowed. |
||||||
Where the client is one router hop away from the DHCP server, only the Option 82 field from the first (and only) relay agent is used to determine the policy boundary for the server response. Where there are multiple Option 82 router hops between the client and the server, you can use different configuration options on different relay agents to achieve the results you want. This includes configuring the relay agents so that the client request arrives at the server with either one Option 82 field or multiple fields. (Using multiple Option 82 fields assumes that the server supports multiple fields and is configured to assign IP addressing policies based on the content of multiple fields.)
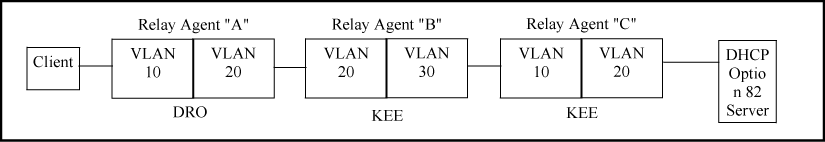
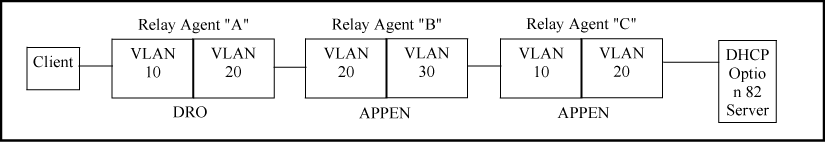
The above combination allows for detection and dropping of client requests with spurious Option 82 fields. If none are found, the drop policy on the first relay agent adds an Option 82 field, which is then kept unchanged over the next two relay agent hops ("B" and "C".) The server can then enforce an IP addressing policy based on the Option 82 field generated by the edge relay agent ("A".) In this example, the DHCP policy boundary is at relay agent 1.
This is an enhancement of the previous example. In this case, each hop for an accepted client request adds a new Option 82 field to the request. A DHCP server capable of using multiple Option 82 fields can be configured to use this approach to keep a more detailed control over leased IP addresses. In this example, the primary DHCP policy boundary is at relay agent "A," but more global policy boundaries can exist at relay agents "B" and "C."
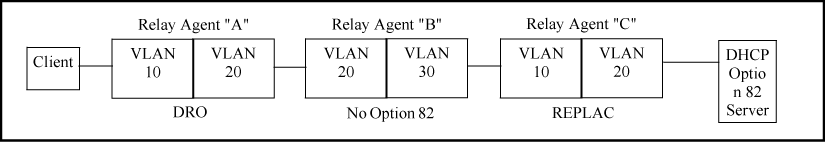
Like the first example, above, this configuration drops client requests with spurious Option 82 fields from clients on the edge relay agent. However, in this case, only the Option 82 field from the last relay agent is retained for use by the DHCP server. In this case the DHCP policy boundary is at relay agent "C." In the previous two examples the boundary was with relay "A."
A valid Option 82 server response to a client request packet includes a copy of the Option 82 fields the server received with the request. With validation disabled, most variations of Option 82 information are allowed, and the corresponding server response packets are forwarded.
Server response validation is an option you can specify when configuring Option 82 DHCP for appendreplacedrop
With validation enabled, the relay agent applies stricter rules to variations in the Option 82 fields of incoming server responses to determine whether to forward the response to a downstream device or to drop the response due to invalid (or missing) Option 82 information. Relay agent management of DHCP server response packets., below, describes relay agent management of DHCP server responses with optional validation enabled and disabled
Relay agent management of DHCP server response packets.
| Response packet content | Option 82 configuration | Validation enabled on the relay agent | Validation disabled (the default) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valid DHCP server response packet without an Option 82 field. | append, replace, or drop[a] |
Drop the server response packet. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. |
keep[b] |
Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | |
| The server response packet carries data indicating a given routing switch is the primary relay agent for the original client request, but the associated Option 82 field in the response contains a remote ID and circuit ID combination that did not originate with the given relay agent. | append |
Drop the server response packet. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. |
replace or drop[a] |
Drop the server response packet. | Drop the server response packet. | |
keep[b] |
Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | |
| The server response packet carries data indicating a given routing switch is the primary relay agent for the original client request, but the associated Option 82 field in the response contains a Remote ID that did not originate with the relay agent. | append |
Drop the server response packet. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. |
replace or drop[a] |
Drop the server response packet. | Drop the server response packet. | |
keep[b] |
Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | |
| All other server response packets[c] | append, keep[b], replace, or drop[a] |
Forward server response packet to a downstream device. | Forward server response packet to a downstream device. |
|
[a] [b] A routing switch with DHCP Option 82 enabled with the [c] A routing switch with DHCP Option 82 enabled drops an inbound server response packet if the packet does not have any device identified as the primary relay agent (giaddr=null; see RFC 2131.) |
|||
On a multinetted VLAN, each interface can form an Option 82 policy boundary within that VLAN if the routing switch is configured to use IP for the remote ID suboption. That is, if the routing switch is configured with IP as the remote ID option and a DHCP client request packet is received on a multinetted VLAN, the IP address used in the Option 82 field will identify the subnet on which the packet was received instead of the IP address for the VLAN. This enables an Option 82 DHCP server to support more narrowly defined DHCP policy boundaries instead of defining the boundaries at the VLAN or whole routing switch levels. If the MAC address option (the default) is configured instead, the routing switch MAC address will be used regardless of which subnet was the source of the client request. (The MAC address is the same for all VLANs configured on the routing switch.)
All request packets from DHCP clients in the different subnets in the VLAN must be able to reach any DHCP server identified by the IP helper addresses configured on that VLAN.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.gif)