For more information, see Assigning the routing switch to OSPF areas.
Syntax:
After using
router ospfto globally enable OSPF and enter the global OSPF context, execute this command to assign the routing switch to a backbone or other normal area.The
noform of the command removes the routing switch from the specified area.Default: No areas; Range: 1 to16 areas (of all types)
Example
Syntax:
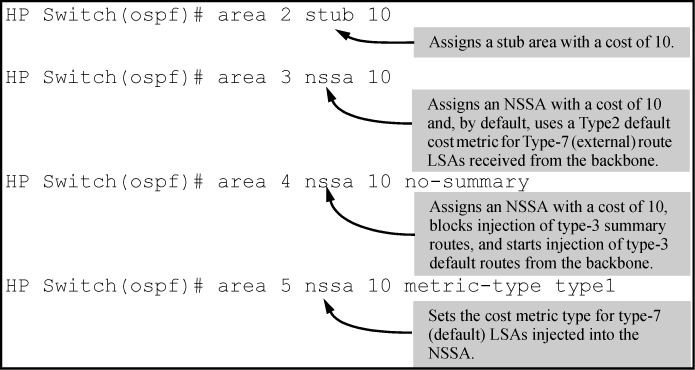
area[no-summary]ospf-area-idstub 0-16777215area[no-summary] [metric-type[ type1 | type2 ]]ospf-area-idnssa 0-16777215No areaospf-area-idAfter using
router ospfto globally enable OSPF and enter the global OSPF context, execute this command to assign the routing switch to a stub area or NSSA. (Does not apply to backbone and normal OSPF area ABRs.)The
noform of the command removes the routing switch from the specified area.Default: No areas; Range: 1 to 16 areas (of all types)
Same area ID as in Configuring an OSPF backbone or normal area, except you cannot assign a backbone area number (
0or0.0.0.0) to a stub or NSSA area.[ stub | nssa ]
Designates the area identified by
ospf-area-idas a stub area or NSSA.If the routing switch is used as an ABR for the designated area, assigns the cost of the default route (to the backbone) that is injected into the area.
NOTE: If the routing switch is not an ABR for the stub area or NSSA, the above cost setting is still required by the CLI, but is not used.
In the default configuration, a routing switch acting as an ABR for a stub area or NSSA injects type-3 summary routes into the area. For an NSSA, the routing switch also injects a type-7 default route into the area.
[no-summary]
Where the routing switch is an ABR for a stub area or an NSSA, this option reduces the amount of link-state advertisement (LSA) traffic entering the area from the backbone by replacing the injection of type-3 summary routes with injection of a type-3 default summary route.
For NSSAs, this command also disables injection of the type-7 default external route from the backbone into the area (included in the
metric-typeoperation described below.)For more information, see Not-so-stubby-area (NSSA), Stub area, and Replacing type-3summary LSAs and type-7 default external LSAs with a type-3 default route LSA.
[metric-type[ type1 | type2 ]]
Enables injection of the type-7 default external route and type-3 summary routes into the area instead of a type 3 default route. Also specifies the type of internal cost metric to include in type-7 LSAs advertised for redistribution of external routes in the NSSA. (The redistribution—or external—cost metric is a global setting on the routing switch set by the
default-metriccommand.)The
metric-typecommand specifies whether to include the redistribution cost in the cost metric calculation for a type-7 default LSA injected into the area.
type1Calculate external route cost for a type-7 default LSA as the sum of (1) the external route cost assigned by the ASBR plus (2) the internal cost from the router with traffic for the external route to the ASBR advertising the route.
type2Calculate external route cost for a type-7 default LSA as being only the cost from the router with traffic for the external route to the ASBR advertising the route.
If metric-type is not specified, the default (
type2) will be used.Using the
areawithout entering eitherospf-area-idnssa 0-16777215no-summaryormetric-typeresets the routing switch to the state where injection of type-3 summary routes and the type-7 default external routes is enabled withmetric-typeset totype2.Default: Enabled with
metric-typetype2
NOTE: Different routers in the NSSA can be configured with different
metric-typevalues.
Examples
After you define an OSPF area (page A-25), you can assign one or more VLANs and/or subnets to it. When a VLAN is assigned to an area, all currently configured IP addresses in that VLAN are automatically included in the assignment unless you enter a specific IP address.
|
|
|
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.gif) |
NOTE: All static VLANs configured on a routing switch configured for OSPF must be assigned to one of the defined areas in the AS. |
|
|
Syntax:
Executed in a specific VLAN context to assign the VLAN or individual subnets in the VLAN to the specified area. Requires that the area is already configured on the routing switch (page A-25.)
When executed without specifying an IP address or using the
allkeyword, this command assigns all configured networks in the VLAN to the specified OSPF area.
Example
To assign VLAN 8 on a routing switch to area 3 and include all IP addresses configured in the VLAN, enter the following commands:
HP Switch(ospf)# vlan 8 HP Switch(vlan-8)# ip ospf area 3Suppose that a system operator wants to assign the three subnets configured in VLAN 10 as shown below:
10.10.10.1 to OSPF area 5
10.10.11.1 to OSPF area 5
10.10.12.1 to OSPF area 6
The operator could use the following commands to configure the above assignments:
HP Switch(ospf)# vlan 10 HP Switch(vlan-10)# ip ospf 10.10.10.1 area 5 HP Switch(vlan-10)# ip ospf 10.10.11.1 area 5 HP Switch(vlan-10)# ip ospf 10.10.12.1 area 6
Optional: After you define the OSPF areas to which the switch belongs, you can assign a user-defined loopback address to an OSPF area. A loopback interface is a virtual interface configured with an IP address and is always reachable as long as at least one of the IP interfaces on the switch is operational. Because the loopback interface is always up, you ensure that the switch's router ID remains constant and that an OSPF network is protected from changes caused by downed interfaces.
For more information, see the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch.
Syntax:
Executed in a specific loopback context to assign a loopback interface to the specified OSPF area. Requires that the specified loopback interface is already configured with an IP address on the switch.
Example:
To assign user-defined loopback interface 3 on the switch to area 192.5.0.0 and include the loopback IP address 172.16.112.2 in the OSPF broadcast area, enter the following commands:
HP Switch(config)# interface loopback 3 HP Switch(lo-3)# ip ospf 172.16.112.2 area 192.5.0.0
Syntax:
Executed in a specific loopback context to modify the cost used to advertise the loopback address (and subnet) to the area border router (ABR.) Requires that the specified loopback interface is already configured with an IP address on the switch.
Example
To configure a cost of 10 for advertising the IP address 172.16.112.2 configured for loopback interface 3 in an OSPF area 192.5.0.0, enter the following commands:
HP Switch(config)# interface loopback 3 HP Switch(lo-3)# ip ospf 172.16.112.2 area 192.5.0.0 HP Switch(lo-3)# ip ospf 172.16.112.2 cost 10
When you assign a loopback address to an OSPF area, the route redistribution of the loopback address is limited to the specified area.
When route redistribution is enabled:
-
The switch advertises a loopback IP address that is not assigned to an OSPF area as an OSPF external route to its OSPF neighbors, and handles it as a connected route.
-
The switch advertises a loopback address that is assigned to an OSPF area as an OSPF internal route.
To enable redistribution of loopback IP addresses in OSPF, enter the redistribution connected command as described in Enabling route redistribution.
Example
Assigning loopback IP addresses to OSPF areas
The loopback IP address 13.3.4.5 of loopback 2 is advertised only in OSPF area 0.0.0.111. The IP addresses 14.2.3.4 and 15.2.3.4 of loopback 1 are advertised in all OSPF areas. The lines in bold below show that the IP address of loopback interface 2 is assigned to OSPF area 111.
HP Switch(config)# interface loopback 1 HP Switch(lo-1)# ip address 14.2.3.4 HP Switch(lo-1)# ip address 15.2.3.4 HP Switch(lo-1)# exit HP Switch(config)# interface loopback 2 HP Switch(lo-2)# ip address 13.3.4.5 HP Switch(lo-2)# ip ospf 15.2.3.4 area 0.0.0.111 HP Switch(lo-2)# exitVerifying OSPF redistribution of loopback interfaces
To verify the OSPF redistribution of loopback interfaces, enter the
show ip routecommand from any context level to display IP route table entries.In this example, a loopback address assigned to an area is displayed as an
ospf intra-area(internal) route to its neighbor; a loopback address not assigned to a specific area is displayed as anospf externalroute:HP Switch(config)# show ip route IP Route Entries Destination Gateway VLAN Type Sub-Type Metric Dist ----------- ------- ---- ---- -------- ------ ---- 20.0.15.1/32 25.0.67.131 25 ospf external2 10 110 20.0.16.2/32 25.0.67.131 25 ospf intra-area 2 110