Custom DHCP options
Some options, such as Option 43, Option 82, and Option 184, have no standard definitions in RFC 2132.
Vendor-specific option (Option 43)
DHCP servers and clients use Option 43 to exchange vendor-specific configuration information.
The DHCP client can obtain the following information through Option 43:
ACS parameters, including the ACS URL, username, and password.
Service provider identifier, which is acquired by the CPE from the DHCP server and sent to the ACS for selecting vender-specific configurations and parameters.
PXE server address, which is used to obtain the boot file or other control information from the PXE server.
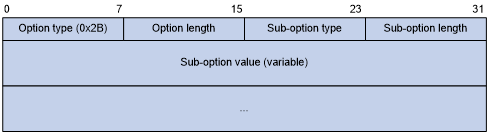
Format of Option 43:
Figure 13: Option 43 format
Network configuration parameters are carried in different sub-options of Option 43 as shown in Figure 13.
Sub-option type—The field value can be 0x01 (ACS parameter sub-option), 0x02 (service provider identifier sub-option), or 0x80 (PXE server address sub-option).
Sub-option length—Excludes the sub-option type and sub-option length fields.
Sub-option value—The value format varies with sub-options.
Sub-option value field formats:
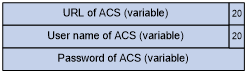
ACS parameter sub-option value field—Includes the ACS URL, username, and password separated by spaces (0x20) as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14: ACS parameter sub-option value field
Service provider identifier sub-option value field—Includes the service provider identifier.
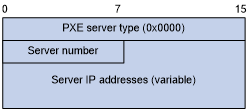
PXE server address sub-option value field—Includes the PXE server type that can only be 0, the server number that indicates the number of PXE servers contained in the sub-option and server IP addresses, as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15: PXE server address sub-option value field
Relay agent option (Option 82)
Option 82 is the relay agent option. It records the location information about the DHCP client. When a DHCP relay agent or DHCP snooping device receives a client's request, it adds Option 82 to the request message and sends it to the server.
The administrator can use Option 82 to locate the DHCP client and further implement security control and accounting. The DHCP server can use Option 82 to provide individual configuration policies for the clients.
Option 82 can include up to 255 sub-options and must have one sub-option at least. Option 82 supports two sub-options: sub-option 1 (Circuit ID) and sub-option 2 (Remote ID).
Option 82 has no standard definition. Its padding formats vary with vendors.
Circuit ID has the following padding formats:
String padding format—Includes a character string specified by the user.
Normal padding format—Includes the VLAN ID and interface number of the interface that received the client's request.
Verbose padding format—Includes the access node identifier specified by the user, and the VLAN ID, interface number and interface type of the interface that received the client's request.
Remote ID has the following padding formats:
String padding format—Includes a character string specified by the user.
Normal padding format—Includes the MAC address of the DHCP relay agent interface or the MAC address of the DHCP snooping device that received the client's request.
Sysname padding format—Includes the device name of the device. To set the device name for the device, use the sysname command in system view.
Option 184
Option 184 is a reserved option. You can define the parameters in the option as needed. The device supports Option 184 carrying voice related parameters, so a DHCP client with voice functions can get voice parameters from the DHCP server.
Option 184 has the following sub-options:
Sub-option 1—Specifies the IP address of the primary network calling processor, which serves as the network calling control source and provides program download services. For Option 184, you must define sub-option 1 to make other sub-options take effect.
Sub-option 2—Specifies the IP address of the backup network calling processor. DHCP clients contact the backup processor when the primary one is unreachable.
Sub-option 3—Specifies the voice VLAN ID and the result whether or not the DHCP client takes this VLAN as the voice VLAN.
Sub-option 4—Specifies the failover route that includes the IP address and the number of the target user. A SIP VoIP user uses this IP address and number to directly establish a connection to the target SIP user when both the primary and backup calling processors are unreachable.