Example: Configuring IRDP
Network configuration
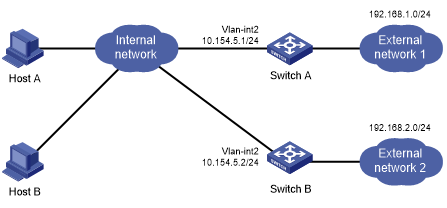
As shown in Figure 55, Host A and Host B that run Linux support IRDP, and they are in the internal network. Switch A and Switch B act as the egress routers and connect to external networks 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24, respectively.
Configure Switch A as the default gateway for the hosts. Packets to the external networks can be correctly routed.
Figure 55: Network diagram
Procedure
![[IMPORTANT: ]](images/important.png) | IMPORTANT: By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface. | |
Configure Switch A:
# Specify an IP address for VLAN-interface 2.
<SwitchA> system-view [SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip address 10.154.5.1 24
# Enable IRDP on VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp
# Specify preference 1000 for advertised IP addresses on VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp preference 1000
# Specify the multicast address 224.0.0.1 as the destination IP address for RAs sent by VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp multicast
# Specify the IP address 192.168.1.0 and preference 400 for VLAN-interface 2 to proxy-advertise.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp address 192.168.1.0 400
Configure Switch B:
# Specify an IP address for VLAN-interface 2.
<SwitchB> system-view [SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] ip address 10.154.5.2 24
# Enable IRDP on VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp
# Specify preference 500 for advertised IP addresses on VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp preference 500
# Specify the multicast address 224.0.0.1 as the destination IP address for RAs sent by VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp multicast
# Specify the IP address 192.168.2.0 and preference 400 for VLAN-interface 2 to proxy-advertise.
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] ip irdp address 192.168.2.0 400
Verifying the configuration
# Display the routing table for Host A.
[HostA@localhost ~]$ netstat -rne Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 10.154.5.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 0.0.0.0 10.154.5.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
The output shows that the default route on Host A points to IP address 10.154.5.1, and Host A has routes to 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24.
# Display the routing table for Host B.
[HostB@localhost ~]$ netstat -rne Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 10.154.5.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 0.0.0.0 10.154.5.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
The output shows that the default route on Host B points to IP address 10.154.5.1, and Host B has routes to 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24.