VSI manipulation
MAC authentication support for VXLANs
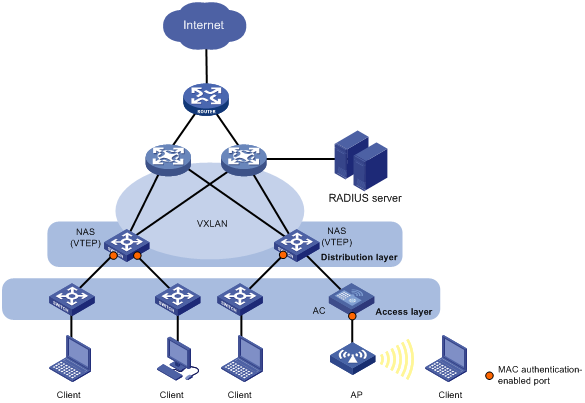
As shown in Figure 45, when the device acts as both a VXLAN VTEP and a NAS, users' service information cannot be identified by VLANs. To resolve this issue, you must configure the RADIUS server to assign VSIs to MAC authenticated users. The NAS will map a user's traffic to the VXLAN that is associated with the user's authorization VSI. The mapping criteria include the user's access VLAN, access port, and MAC address.
For information about VSIs and VXLANs, see VXLAN Configuration Guide.
Figure 45: VXLAN network diagram for MAC authentication
Authorization VSI
An authorization VSI is associated with a VXLAN that has network resources inaccessible to unauthenticated users.
MAC authentication supports remote VSI authorization. If the VTEP does not receive authorization VSI information for a MAC authentication user from the remote server, the user cannot access resources in any VXLAN after passing authentication. If the VTEP receives authorization VSI information for the user from the remote server, it performs the following operations:
Dynamically creates an Ethernet service instance according to the user's access port, VLAN, and MAC address.
Maps the Ethernet service instance to the authorization VSI.
The user then can access resources in the VXLAN associated with the authorization VSI.
For information about dynamic creation of Ethernet service instances, see VXLAN configuration Guide.
Guest VSI
The MAC authentication guest VSI on a port accommodates users that have failed MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. For example, the VSI accommodates users with invalid passwords entered.
You can deploy a limited set of network resources in the VXLAN that is associated with the MAC authentication guest VSI. For example, a software server for downloading software and system patches.
Table 16 shows the way that the VTEP handles guest VSIs for MAC authentication users.
Table 16: VSI manipulation
Authentication status | VSI manipulation |
|---|---|
A user fails MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. | The VTEP maps the user's MAC address and access VLAN to the MAC authentication guest VSI. |
A user in the MAC authentication guest VSI fails MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. | The user is still in the MAC authentication guest VSI. |
A user in the MAC authentication guest VSI passes MAC authentication. | The VTEP remaps the user's MAC address and access VLAN to the authorization VSI assigned by the authentication server. |
Critical VSI
The MAC authentication critical VSI on a port accommodates users that have failed MAC authentication because no RADIUS authentication servers are reachable. Users in a MAC authentication critical VSI can access only network resources in the VXLAN associated with this VSI.
The critical VSI feature takes effect when MAC authentication is performed only through RADIUS servers. If a MAC authentication user fails local authentication after RADIUS authentication, the user is not assigned to the critical VSI. For more information about the authentication methods, see "Configuring AAA."
Table 17 shows the way that the VTEP handles critical VSIs for MAC authentication users.
Table 17: VSI manipulation
Authentication status | VSI manipulation |
|---|---|
A user fails MAC authentication because all the RADIUS servers are unreachable. | The VTEP maps the user's MAC address and access VLAN to the MAC authentication critical VSI. The user is still in the MAC authentication critical VSI if the user fails MAC reauthentication because all the RADIUS servers are unreachable. If no MAC authentication critical VSI is configured, the device logs off the user. |
A user in the MAC authentication critical VSI fails MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. | If a guest VSI has been configured, the VTEP maps the user's MAC address and access VLAN to the guest VSI. If no guest VSI is configured, the VTEP logs off the user. |
A user in the MAC authentication critical VSI passes MAC authentication. | The VTEP remaps the user's MAC address and access VLAN to the authorization VSI assigned by the authentication server. |