IGMP proxying
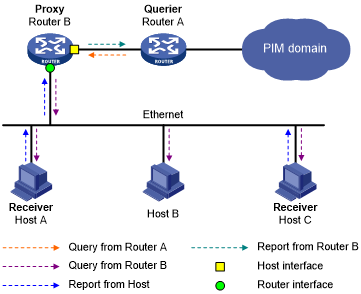
As shown in Figure 37, in a simple tree-shaped topology, it is not necessary to run multicast routing protocols, such as PIM, on edge devices. Instead, you can configure IGMP proxying on these devices. With IGMP proxying configured, the edge device acts as an IGMP proxy:
For the upstream IGMP querier, the IGMP proxy device acts as a host.
For the downstream receiver hosts, the IGMP proxy device acts as an IGMP querier.
Figure 37: IGMP proxying
The following types of interfaces are defined in IGMP proxying:
Host interface—An interface that is in the direction toward the root of the multicast forwarding tree. A host interface acts as a receiver host that is running IGMP. IGMP proxying must be enabled on this interface. This interface is also called the "proxy interface."
Router interface—An interface that is in the direction toward the leaf of the multicast forwarding tree. A router interface acts as a router that is running IGMP. IGMP must be configured on this interface.
An IGMP proxy device maintains a group membership database, which stores the group memberships on all the router interfaces. The host interfaces and router interfaces perform actions based on this membership database.
The host interfaces respond to queries according to the membership database or send join/leave messages when the database changes.
The router interfaces participate in the querier election, send queries, and maintain memberships based on received IGMP reports.