IGMP snooping ports
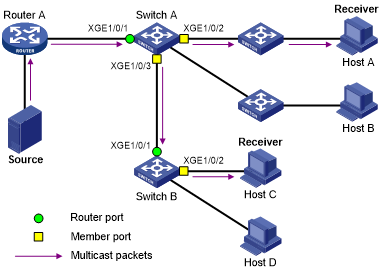
As shown in Figure 12, IGMP snooping runs on Switch A and Switch B, and Host A and Host C are receivers in a multicast group. IGMP snooping ports are divided into member ports and router ports.
Figure 12: IGMP snooping ports
Router ports
On an IGMP snooping Layer 2 device, the ports toward Layer 3 multicast devices are called router ports. In Figure 12, Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Switch A and Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Switch B are router ports.
Router ports contain the following types:
Dynamic router port—When a port receives an IGMP general query whose source address is not 0.0.0.0 or receives a PIM hello message, the port is added into the dynamic router port list. At the same time, an aging timer is started for the port. If the port receives either of the messages before the timer expires, the timer is reset. If the port does not receive either of the messages when the timer expires, the port is removed from the dynamic router port list.
Static router port—When a port is statically configured as a router port, it is added into the static router port list. The static router port does not age out, and it can be deleted only manually.
Do not confuse the "router port" in IGMP snooping with the "routed interface" commonly known as the "Layer 3 interface." The router port in IGMP snooping is a Layer 2 interface.
Member ports
On an IGMP snooping Layer 2 device, the ports toward receiver hosts are called member ports. In Figure 12, Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 of Switch A and Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 of Switch B are member ports.
Member ports contain the following types:
Dynamic member port—When a port receives an IGMP report, it is added to the associated dynamic IGMP snooping forwarding entry as an outgoing interface. At the same time, an aging timer is started for the port. If the port receives an IGMP report before the timer expires, the timer is reset. If the port does not receive an IGMP report when the timer expires, the port is removed from the associated dynamic forwarding entry.
Static member port—When a port is statically configured as a member port, it is added to the associated static IGMP snooping forwarding entry as an outgoing interface. The static member port does not age out, and it can be deleted only manually.
Unless otherwise specified, router ports and member ports in this document include both static and dynamic router ports and member ports.