PIM-SSM overview
The ASM model includes PIM-DM and PIM-SM. The SSM model can be implemented by leveraging part of the PIM-SM technique. It is also called "PIM-SSM."
The SSM model provides a solution for source-specific multicast. It maintains the relationship between hosts and routers through IGMPv3.
In actual applications, part of IGMPv3 and PIM-SM techniques are adopted to implement the SSM model. In the SSM model, because receivers have located a multicast source, no RP or RPT is required. Multicast sources do not register with the RP, and the MSDP is not needed for discovering multicast sources in other PIM domains.
Neighbor discovery
PIM-SSM uses the same neighbor discovery mechanism as PIM-SM. For more information, see "Neighbor discovery."
DR election
PIM-SSM uses the same DR election mechanism as PIM-SM. For more information, see "DR election."
SPT building
The decision to build an RPT for PIM-SM or an SPT for PIM-SSM depends on whether the multicast group that the multicast receiver joins is in the SSM group range. The SSM group range reserved by IANA is 232.0.0.0/8.
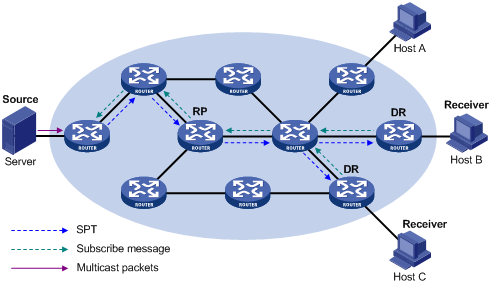
Figure 45: SPT building in PIM-SSM
As shown in Figure 45, Host B and Host C are receivers. They send IGMPv3 report messages to their DRs to express their interest in the multicast information that the multicast source S sends to the multicast group G.
After receiving a report message, the DR first checks whether the group address in this message is in the SSM group range and does the following:
If the group address is in the SSM group range, the PIM-SSM service is provided.
The DR sends a subscribe message toward the multicast source. All routers along the path from the DR to the source create an (S, G) entry to build an SPT. The SPT is rooted at the multicast source S and has the receivers as its leaves.
If the group address is not in the SSM group range, the PIM-SM service is provided.
The receiver-side DR sends a (*, G) join message to the RP, and the multicast source registers with the source-side DR.
In PIM-SSM, the term "channel" refers to a multicast group, and the term "subscribe message" refers to a join message.