How QinQ works
The devices in the public network forward a frame only according to its outer VLAN tag and obtain its source MAC address into the MAC address table of the outer VLAN. The inner VLAN tag of the frame is transmitted as the payload.
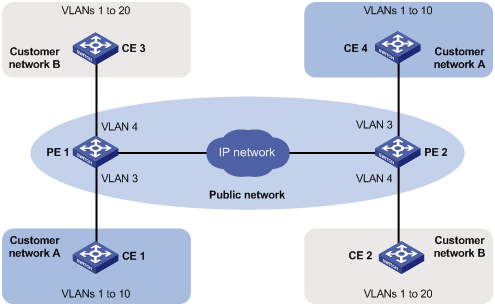
Figure 62: Typical QinQ application scenario
As shown in Figure 62, customer network A has CVLANs 1 through 10, and customer network B has CVLANs 1 through 20. The service provider assigns SVLAN 3 for customer network A, and assigns SVLAN 4 for customer network B.
When a tagged Ethernet frame from customer network A arrives at a provider edge device (PE), the PE tags the frame with outer VLAN 3. When a tagged Ethernet frame from customer network B arrives at a PE, the PE tags the frame with outer VLAN 4. There is no overlap of VLAN IDs among customers, and traffic from different customers can be identified separately.
The double-tagged Ethernet frame is then transmitted over the service provider network and arrives at the other PE. The PE removes the SVLAN of the frame before sending it to the target customer edge device (CE).