802.1X with EAD assistant configuration example
Network requirements
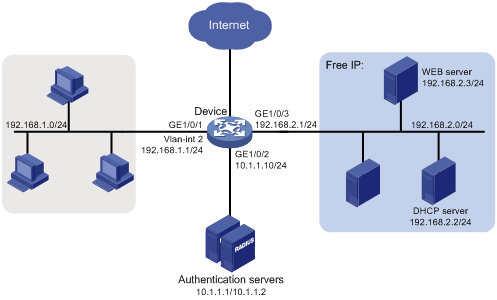
As shown in Figure 33:
The intranet 192.168.1.0/24 is attached to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the access device.
The hosts use DHCP to obtain IP addresses.
A DHCP server and a Web server are deployed on the 192.168.2.0/24 subnet for users to obtain IP addresses and download client software.
Deploy an EAD solution for the intranet to meet the following requirements:
Allow unauthenticated users and users who have failed 802.1X authentication to access 192.168.2.0/24. The users can obtain IP addresses and download software.
If these users use a Web browser to access a network other than 192.168.2.0/24, redirect them to the Web server for 802.1X client downloading.
Allow authenticated 802.1X users to access the network.
Figure 33: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Make sure the DHCP server, the Web server, and the authentication servers have been configured correctly. (Details not shown.)
Configure an IP address for each interface. (Details not shown.)
Configure DHCP relay:
# Enable DHCP.
<Device> system-view [Device] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP relay agent on VLAN-interface 2.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 2 [Device-Vlan-interface2] dhcp select relay
# Specify the DHCP server 192.168.2.2 on the relay agent interface VLAN-interface 2.
[Device-Vlan-interface2] dhcp relay server-address 192.168.2.2 [Device-Vlan-interface2] quit
Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create RADIUS scheme 2000 and enter RADIUS scheme view.
[Device] radius scheme 2000
# Specify the server at 10.1.1.1 as the primary authentication server, and set the authentication port to 1812.
[Device-radius-2000] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 1812
# Specify the server at 10.1.1.2 as the primary accounting server, and set the accounting port to 1813.
[Device-radius-2000] primary accounting 10.1.1.2 1813
# Set the shared key to abc in plain text for secure communication between the authentication server and the device.
[Device-radius-2000] key authentication simple abc
# Set the shared key to abc in plain text for secure communication between the accounting server and the device.
[Device-radius-2000] key accounting simple abc
# Exclude the ISP domain name from the usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
[Device-radius-2000] user-name-format without-domain [Device-radius-2000] quit
Configure an ISP domain:
# Create ISP domain bbb and enter ISP domain view.
[Device] domain bbb
# Apply RADIUS scheme 2000 to the ISP domain for authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[Device-isp-bbb] authentication lan-access radius-scheme 2000 [Device-isp-bbb] authorization lan-access radius-scheme 2000 [Device-isp-bbb] accounting lan-access radius-scheme 2000 [Device-isp-bbb] quit
Configure 802.1X:
# Configure the free IP.
[Device] dot1x ead-assistant free-ip 192.168.2.0 24
# Configure the redirect URL for client software download.
[Device] dot1x ead-assistant url http://192.168.2.3
# Enable the EAD assistant feature.
[Device] dot1x ead-assistant enable
# Enable 802.1X globally.
[Device] dot1x
# Enable 802.1X on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x [Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify the 802.1X configuration.
[Device] display dot1x
# Verify that you can ping an IP address on the free IP subnet from a host.
C:\>ping 192.168.2.3
Pinging 192.168.2.3 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.3:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
The output shows that you can access the free IP subnet before passing 802.1X authentication.
# Verify that you are redirected to the Web server when you enter in your Web browser an IP address not on the free IP. (Details not shown.)