Configuring the MED attribute
BGP uses MED to determine the optimal route for traffic going into an AS. When a BGP router obtains multiple routes with the same destination but with different next hops, it considers the route with the smallest MED value as the optimal route if other conditions are the same.
Configuring the default MED value
To configure the default MED value (IPv4 unicast/multicast address family):
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter BGP IPv4 unicast address family view, BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast address family view, or BGP IPv4 multicast address family view. |
| N/A |
3. Configure the default MED value. | default med med-value | The default MED value is 0. |
To configure the default MED value (IPv6 unicast/multicast address family):
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter BGP IPv6 unicast address family view, BGP-VPN IPv6 unicast address family view, or BGP IPv6 multicast address family view. |
| N/A |
3. Configure the default MED value. | default med med-value | The default MED value is 0. |
Enabling MED comparison for routes from different ASs
This task enables BGP to compare the MEDs of routes from different ASs.
To enable MED comparison for routes from different ASs:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter BGP instance view or BGP-VPN instance view. |
| N/A |
3. Enable MED comparison for routes from different ASs. | compare-different-as-med | By default, MED comparison for routes from different ASs is disabled. |
Enabling MED comparison for routes on a per-AS basis
This task enables BGP to compare the MEDs of routes from an AS.
Figure 62: Route selection based on MED (in an IPv4 network)
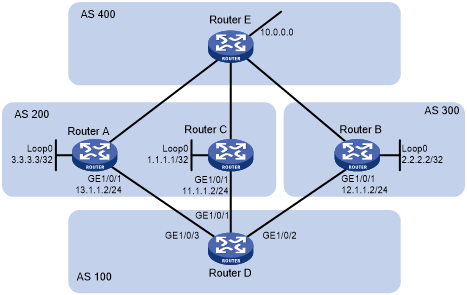
As shown in Figure 62, Router D establishes indirect EBGP peer relationships with Router A, Router B, and Router C, and learns addresses 1.1.1.1/32, 2.2.2.2/32, and 3.3.3.3/32 through OSPF. The following output shows the routing information on Router D.
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 O_INTRA 10 10 11.1.1.2 GE1/0/1 2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 20 12.1.1.2 GE1/0/2 3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 30 13.1.1.2 GE1/0/3
Router D learns network 10.0.0.0 from both Router A and Router B. Because the route learned from Router B has a smaller IGP metric, the route is optimal. The following output shows the BGP routing table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *>e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e * e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e
When Router D learns network 10.0.0.0 from Router C, it compares the route with the optimal route in its routing table. Because Router C and Router B reside in different ASs, BGP does not compare the MEDs of the two routes. The route from Router C has a smaller IGP metric than the route from Router B, so the route from Router C becomes optimal. The following output shows the BGP routing table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *>e 10.0.0.0 1.1.1.1 60 0 200 400e * e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e * e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e
However, Router C and Router A reside in the same AS, and Router C has a greater MED, so network 10.0.0.0 learned from Router C should not be optimal.
To avoid this problem, you can configure the bestroute compare-med command to enable MED comparison for routes from the same AS on Router D. After that, Router D puts the routes received from each AS into a group, selects the route with the lowest MED from each group, and compares routes from different groups. Network 10.0.0.0 learned from Router B is the optimal route. The following output shows the BGP routing table on Router D.
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *>e 10.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 50 0 300 400e * e 3.3.3.3 50 0 200 400e * e 1.1.1.1 60 0 200 400e
To enable MED comparison for routes on a per-AS basis:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter BGP instance view or BGP-VPN instance view. |
| N/A |
3. Enable MED comparison for routes on a per-AS basis. | bestroute compare-med | By default, MED comparison for routes on a per-AS basis is disabled. |
Enabling MED comparison for routes from confederation peers
This task enables BGP to compare the MEDs of routes received from confederation peers. However, if a route received from a confederation peer has an AS number that does not belong to the confederation, BGP does not compare the route with other routes. For example, a confederation has three AS numbers 65006, 65007, and 65009. BGP receives three routes from different confederation peers. The AS_PATH attributes of these routes are 65006 65009, 65007 65009, and 65008 65009, and the MED values of them are 2, 3, and 1. Because the third route's AS_PATH attribute contains AS number 65008 that does not belong to the confederation, BGP does not compare it with other routes. As a result, the first route becomes the optimal route.
To enable MED comparison for routes from confederation peers:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter BGP instance view or BGP-VPN instance view. |
| N/A |
3. Enable MED comparison for routes from confederation peers. | bestroute med-confederation | By default, MED comparison for routes from confederation peers is disabled. |