Configuring LSP parameters
Configuring LSP timers
Specify the maximum age of LSPs.
Each LSP has an age that decreases in the LSDB. Any LSP with an age of 0 is deleted from the LSDB. You can adjust the age value based on the scale of a network.
To specify the maximum age of LSPs:
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter IS-IS view.
isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
3. Specify the maximum LSP age.
timer lsp-max-age seconds
The default setting is 1200 seconds.
Specify the LSP refresh interval and generation interval.
Each router needs to refresh its LSPs at a configurable interval and send them to other routers to prevent valid routes from aging out. A smaller refresh interval speeds up network convergence but consumes more bandwidth.
When network topology changes such as neighbor state, interface metric, system ID, or area ID changes occur, the router generates an LSP after a configurable interval. If such a change occurs frequently, excessive LSPs are generated, consuming a large amount of router resources and bandwidth. To solve the problem, you can adjust the LSP generation interval.
When network changes are not frequent, the minimum-interval is adopted. If network changes become frequent, the LSP generation interval increases by incremental-interval × 2n-2 (n is the number of calculation times) each time a generation occurs until the maximum-interval is reached.
To specify the LSP refresh interval and generation interval:
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter IS-IS view.
isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
3. Specify the LSP refresh interval.
timer lsp-refresh seconds
By default, the LSP refresh interval is 900 seconds.
4. Specify the LSP generation interval.
timer lsp-generation maximum-interval [ minimum-interval [ incremental-interval ] ] [ level-1 | level-2 ]
By default:
The maximum interval is 5 seconds.
The minimum interval is 50 milliseconds.
The incremental interval is 200 milliseconds.
Specify LSP sending intervals.
If a change occurs in the LSDB, IS-IS advertises the changed LSP to neighbors. You can specify the minimum interval for sending these LSPs to control the amount of LSPs on the network.
On a P2P link, IS-IS requires an advertised LSP be acknowledged. If no acknowledgment is received within a configurable interval, IS-IS will retransmit the LSP.
To configure LSP sending intervals:
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
N/A
3. Specify the minimum interval for sending LSPs and the maximum LSP number that can be sent at a time.
isis timer lsp time [ count count ]
By default, the minimum interval is 33 milliseconds, and the maximum LSP number that can be sent at a time is 5.
4. Specify the LSP retransmission interval on a P2P link.
isis timer retransmit seconds
By default, the LSP retransmission interval on a P2P link is 5 seconds.
Specifying LSP lengths
IS-IS messages cannot be fragmented at the IP layer because they are directly encapsulated in frames. IS-IS routers in an area must send LSPs smaller than the smallest interface MTU in the area.
If the IS-IS routers have different interface MTUs, configure the maximum size of generated LSP packets to be smaller than the smallest interface MTU in the area. Without the configuration, the routers must dynamically adjust the LSP packet size to fit the smallest interface MTU, which takes time and affects other services.
To specify LSP lengths:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter IS-IS view. | isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] | N/A |
3. Specify the maximum length of generated Level-1 LSPs or Level-2 LSPs. | lsp-length originate size [ level-1 | level-2 ] | By default, the maximum length of generated Level-1 LSPs or Level-2 LSPs is 1497 bytes. |
4. Specify the maximum length of received LSPs. | lsp-length receive size | By default, the maximum length of received LSPs is 1497 bytes. |
Enabling LSP flash flooding
Changed LSPs can trigger SPF recalculation. To advertise the changed LSPs before the router recalculates routes for faster network convergence, enable LSP flash flooding.
To enable LSP flash flooding:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter IS-IS view. | isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] | N/A |
3. Enable LSP flash flooding. | flash-flood [ flood-count flooding-count | max-timer-interval flooding-interval | [ level-1 | level-2 ] ] * | By default, LSP flash flooding is disabled. |
Enabling LSP fragment extension
Perform this task to enable IS-IS fragment extension for an IS-IS process. The MTUs of all interfaces running the IS-IS process must not be less than 512. Otherwise, LSP fragment extension does not take effect.
To enable LSP fragment extension:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter IS-IS view. | isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] | N/A |
3. Enable LSP fragment extension. | lsp-fragments-extend [ level-1 | level-1-2 | level-2 ] | By default, this feature is disabled. |
4. Configure a virtual system ID. | virtual-system virtual-system-id | By default, no virtual system ID is configured. Configure a minimum of one virtual system to generate extended LSP fragments. |
Limiting LSP flooding
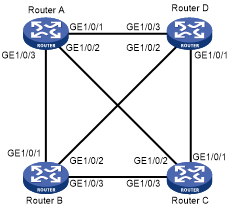
In some networks, many P2P links exist. As shown in Figure 41, Routers A, B, C and D run IS-IS. When Router A generates an LSP, it floods the LSP out of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3. After Router D receives the LSP from GigabitEthernet 1/0/3, it floods it out of GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to Router B and Router C. However, Router B and Router C have already received the LSP from Router A. Repeated LSP flooding consumes extra bandwidth.
Figure 41: Network diagram of a fully meshed network
To avoid this problem, you can add interfaces to a mesh group or block some interfaces.
An interface in a mesh group floods a received LSP only to interfaces not in the mesh group.
A blocked interface sends LSPs only after receiving LSP requests.
Before you configure this task, you must consider redundancy for interfaces in case LSP packets cannot be flooded because of link failures.
To add an interface to a mesh group or block an interface:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enter interface view. | interface interface-type interface-number | N/A |
3. Add the interface to a mesh group or block the interface. |
| By default, the interface does not belong to any mesh group and is not blocked. The mesh group feature takes effect only on P2P interfaces. |