Configuring RIP FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop until RIP completes routing convergence based on the new network topology. FRR enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of link or node failures.
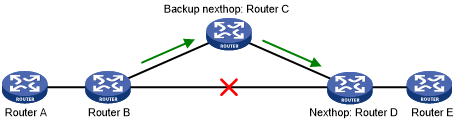
Figure 6: Network diagram for RIP FRR
As shown in Figure 6, configure FRR on Router B by using a routing policy to specify a backup next hop. When the primary link fails, RIP directs packets to the backup next hop. At the same time, RIP calculates the shortest path based on the new network topology, and forwards packets over that path after network convergence.