VoIP system
For POTS, all functions from the call originator to the call receiver are implemented by the public switched telephone network (PSTN). VoIP functions differently from POTS, as described in this section.
Figure 1: VoIP system
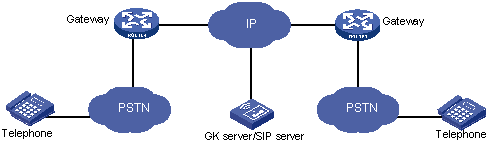
In Figure 1, the VoIP gateway provides interfaces for communication between the IP network and PSTN/ISDN. Users connect to the originating VoIP gateway through PSTN. The originating VoIP gateway converts analog signals into digital signals and compresses them into voice packets that can be transmitted over the IP network. The IP network transmits the voice packets to the terminating VoIP gateway, which converts the voice packets back into recognizable analog signals and then transmits them to the receiver. This is a complete telephone-to-telephone communication process. In practice, a gatekeeper (GK) server or SIP server can be applied in the VoIP system to implement functions such as routing and access control.