EtoFR configuration example
Network requirements
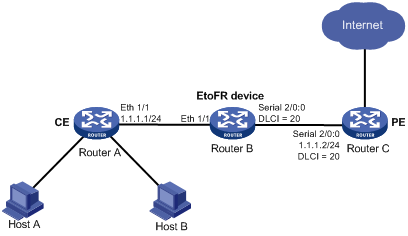
As shown in Figure 119, Router A (the CE) is the gateway for a LAN and is connected to Router B (the EtoFR device) through an Ethernet interface. Router B is connected to Router C (the PE) through an FR-encapsulated serial interface formed by bundling timeslots on a T1 line.
Map the Ethernet interface to the FR interface on Router B through EtoFR to forward traffic between the two interfaces at Layer 2.
Figure 119: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Configure the CE (Router A):
# Configure the IP address of interface Ethernet 1/1 on Router A.
<RouterA> system-view [RouterA] interface ethernet 1/1 [RouterA-Ethernet1/1] ip address 1.1.1.1 24
Configure the PE (Router C):
# Configure the IP address of the synchronous serial interface formed by timeslot bundling on interface T1 2/0.
<RouterC> system-view [RouterC] controller t1 2/0 [RouterC-T1 2/0] channel-set 0 timeslot-list 1-24 [RouterC-T1 2/0] quit [RouterC] interface serial 2/0:0 [RouterC-Serial2/0:0] link-protocol fr [RouterC-Serial2/0:0] fr interface-type dce [RouterC-Serial2/0:0] fr dlci 20 [RouterC-Serial2/0:0] ip address 1.1.1.2 24
Configure the EtoFR device (Router B):
# Create the EtoFR mapping for forwarding the traffic between the CE and the PE.
<RouterB> system-view [RouterB] controller t1 2/0 [RouterB-T1 2/0] channel-set 0 timeslot-list 1-24 [RouterB-T1 2/0] quit [RouterB] interface serial 2/0:0 [RouterB-Serial2/0:0] link-protocol fr [RouterB-Serial2/0:0] fr dlci 20 [RouterB-Serial2/0:0] quit [RouterB] etofr translate interface ethernet 1/1 serial 2/0:0 dlci 20 ip-address 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.2
If Inverse ARP (InARP) is disabled on interface Serial 2/0:0 on the PE, you must manually configure an FR address mapping for the Serial 2/0:0 interfaces with the fr map ip command on the PE and the EtoFR device.