Approaches to DCC
Two approaches are available to DCC: circular DCC (C-DCC) and resource-shared DCC (RS-DCC). They are suitable for different applications. In practice, the two parties in a call do not necessarily adopt the same approach.
Terms used in DCC configuration are as follows:
Physical interface—An interface that physically exists. Examples are serial, BRI, and asynchronous interfaces.
Dialer interface—A logical interface created for configuring DCC parameters. A physical interface can inherit the DCC configurations after it is assigned to a dialer interface.
Dialup interface—Any interface used for dialup connection. It can be a dialer interface, a physical interface assigned to a dialer interface, or a physical interface directly configured with DCC parameters.
C-DCC
Features of C-DCC.
C-DCC delivers the following features:
A logical dial (dialer) interface can contain multiple physical interfaces, but a physical interface can be assigned to only one dialer interface. A physical interface can provide only one type of dial service.
You can assign a physical interface to a dialer interface to inherit DCC parameters by assigning it to a dialer circular group, or directly configure DCC parameters on the physical interface.
All the physical interfaces in a dialer circular group inherit the attributes of the same dialer interface.
You can associate a dialer interface with multiple call destination addresses by configuring the dialer route command or with a single call destination address by configuring the dialer number command.
C-DCC is powerful and has broad applications. However, it lacks flexibility and extensibility.
For example, on an ISDN BRI interface, all the B channels inherit its configuration in the C-DCC approach. The static binding between call destination address settings and physical interface configurations will restrict using C-DCC, because dialer routes are becoming increasingly complicated as a result of network growth and support to more protocols.
Association of physical interfaces and dialer interfaces in C-DCC.
Figure 38: Association between physical interfaces and dialer interfaces
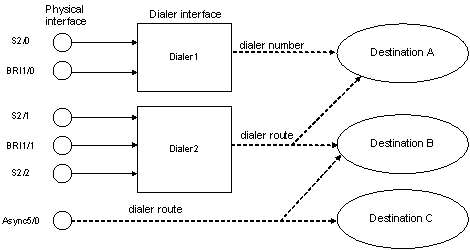
In Figure 38, a physical interface can be assigned to only one dialer interface, but each dialer interface can contain multiple physical interfaces and be mapped to multiple destination addresses. In addition, a physical interface does not necessarily belong to any dialer interface. You can directly map it to one or multiple destination addresses.
In the figure, physical interfaces Serial 2/1, BRI 1/1, and Serial 2/2 are assigned to Dialer2, where mappings between dial strings and destination addresses are configured.
RS-DCC
Features of RS-DCC.
RS-DCC is different from C-DCC and separates logical configuration from physical configuration, so it is simpler and more flexible. RS-DCC delivers the following features:
Physical interface configuration and logical configuration for calls are separate. They are associated dynamically when triggered by calls. This allows a physical interface to provide services for different dial applications.
Associations between dialer interfaces and call destination addresses are one-to-one. You can configure them with the dialer number command.
Each dialer interface can contain multiple physical interfaces, and each physical interface can be assigned to multiple dialer interfaces.
Dial attributes, such as dialer interface, dialer bundle, and physical interface, are described by an RS-DCC set. All the calls destined to the same network use the same RS-DCC set.
RS-DCC parameters cannot be directly configured on physical interfaces. A physical interface can participate in RS-DCC only after it is assigned to a dialer interface.
Association of physical interfaces, dialer bundles, and dialer interfaces in RS-DCC.
Figure 39: Association of physical interfaces, dialer bundles, and dialer interfaces
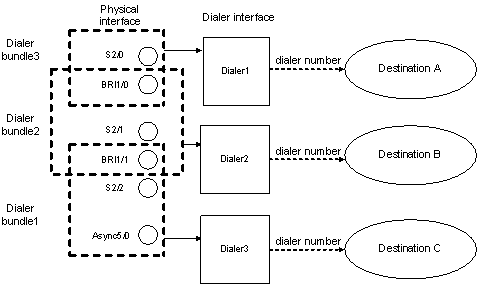
In Figure 39, a physical interface can be assigned to multiple dialer bundles and serve multiple dialer interfaces, but each dialer interface can use only one dialer bundle and configured with one dial string. The physical interfaces in a dialer bundle can be assigned different priorities.
In the figure, interface Dialer2 uses dialer bundle 2, which contains physical interfaces BRI 1/0, BRI 1/1, and Serial 2/1. Suppose BRI 1/0 is assigned the priority of 100, BRI 1/1 the priority of 50, and Serial 2/1 the priority of 75. Because BRI 1/0 has a higher priority over BRI 1/1 and Serial 2/1, it will be preferred when Dialer2 places a call.