FRR configuration example
Network requirements
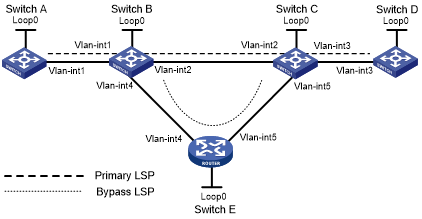
On the primary CRLSP Switch A—Switch B—Switch C—Switch D, use FRR to protect the link Switch B—Switch C.
Use RSVP-TE to establish the primary CRLSP and bypass CRLSP of the MPLS TE tunnel based on the constraints of the explicit paths. The bypass CRLSP uses path Switch B—Switch E—Switch C. Switch B is the PLR and Switch C is the MP.
Configure BFD for RSVP-TE between Switch B and Switch C. When the link between Switch B and Switch C fails, BFD can detect the failure quickly and notify RSVP-TE of the failure, so RSVP-TE can switch traffic to the bypass CRLSP.
Figure 26: Network diagram
Table 4: Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Switch A | Loop0 | 1.1.1.1/32 | Switch E | Loop0 | 5.5.5.5/32 |
Vlan-int1 | 2.1.1.1/24 | Vlan-int4 | 3.2.1.2/24 | ||
Switch B | Loop0 | 2.2.2.2/32 | Vlan-int5 | 3.3.1.1/24 | |
Vlan-int1 | 2.1.1.2/24 | Switch C | Loop0 | 3.3.3.3/32 | |
Vlan-int2 | 3.1.1.1/24 | Vlan-int3 | 4.1.1.1/24 | ||
Vlan-int4 | 3.2.1.1/24 | Vlan-int2 | 3.1.1.2/24 | ||
Switch D | Loop0 | 4.4.4.4/32 | Vlan-int5 | 3.3.1.2/24 | |
Vlan-int3 | 4.1.1.2/24 |
Configuration procedure
Configure IP addresses and masks for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
Configure IS-IS to advertise interface addresses, including the loopback interface address. (Details not shown.)
Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE on each switch, and enable BFD for RSVP-TE on Switch B and Switch C:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view [SwitchA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [SwitchA] mpls te [SwitchA-te] quit [SwitchA] rsvp [SwitchA-rsvp] quit [SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 1 [SwitchA-Vlan-interface1] mpls enable [SwitchA-Vlan-interface1] mpls te enable [SwitchA-Vlan-interface1] rsvp enable [SwitchA-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view [SwitchB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [SwitchB] mpls te [SwitchB-te] quit [SwitchB] rsvp [SwitchB-rsvp] quit [SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 1 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface1] mpls enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface1] mpls te enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface1] rsvp enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface1] quit [SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls te enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] rsvp enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] rsvp bfd enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit [SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 4 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface4] mpls enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface4] mpls te enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface4] rsvp enable [SwitchB-Vlan-interface4] quit
# Configure Switch C in the same way that Switch B is configured. (Details not shown.)
# Configure Switch D and Switch E in the same way that Switch A is configured. (Details not shown.)
Configure an MPLS TE tunnel on Switch A, the ingress node of the primary CRLSP:
# Configure an explicit path for the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] explicit-path pri-path [SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 2.1.1.2 [SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 3.1.1.2 [SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 4.1.1.2 [SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 4.4.4.4 [SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] quit
# Create MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 4 for the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] interface tunnel 4 mode mpls-te [SwitchA-Tunnel4] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Switch D.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] destination 4.4.4.4
# Specify the tunnel signaling protocol as RSVP-TE.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
# Specify the explicit path as pri-path.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path pri-path
# Enable FRR for the MPLS TE tunnel.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te fast-reroute [SwitchA-Tunnel4] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel command on Switch A. The output shows that the tunnel interface Tunnel4 is up.
[SwitchA] display interface tunnel Tunnel4 current state: UP Line protocol current state: UP Description: Tunnel3 Interface The Maximum Transmit Unit is 64000 Internet Address is 9.1.1.1/24 Primary Tunnel source unknown, destination 3.3.3.9 Tunnel bandwidth 64 (kbps) Tunnel TTL 255 Tunnel protocol/transport CR_LSP Last clearing of counters: Never Last 300 seconds input rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec Last 300 seconds output rate: 1911 bytes/sec, 15288 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 drops 1526 packets output, 22356852 bytes, 0 drops# Execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on Switch A to display detailed information about the MPLS TE tunnel.
[SwitchA] display mpls te tunnel-interface Tunnel Name : Tunnel 4 Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP down) Tunnel Attributes : LSP ID : 48960 Tunnel ID : 4 Admin State : Normal Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 3.3.3.3 Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : - Resv Style : SE Tunnel mode : - Reverse-LSP name : - Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: - Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 0 kbps Reserved Bandwidth : 0 kbps Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7 Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0 Explicit Path : pri-path Backup Explicit Path : - Metric Type : TE Record Route : Disabled Record Label : Disabled FRR Flag : Enabled Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: - Backup Bandwidth : - Route Pinning : Disabled Retry Limit : 10 Retry Interval : 2 sec Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : - Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : - Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : - Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : - Collected Bandwidth : -
Configure a bypass tunnel on Switch B (the PLR):
# Configure an explicit path for the bypass tunnel.
[SwitchB] explicit-path by-path [SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.2.1.2 [SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.3.1.2 [SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.3.3.3 [SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] quit
# Create MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 5 for the bypass tunnel.
[SwitchB] interface tunnel 5 mode mpls-te [SwitchB-Tunnel5] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as LSR ID of Switch C.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] destination 3.3.3.3
# Specify the tunnel signaling protocol as RSVP-TE.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
# Specify the explicit path as by-path.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path by-path
# Configure the bandwidth that the bypass tunnel can protect.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te backup bandwidth 10000 [SwitchB-Tunnel5] quit
# Bind the bypass tunnel to the protected interface.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] rsvp fast-reroute bypass-tunnel tunnel 5 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel command on Switch B. The output shows that the tunnel interface Tunnel 5 is up. (Details not shown.)
Configure a static route on Switch A to direct the traffic destined for subnet 4.1.1.0/24 to MPLS TE tunnel 4.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 4.1.1.2 24 tunnel 4 preference 1
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display mpls lsp command on each switch to display LSP entries. The output shows that Switch B and Switch C each have two CRLSPs. The bypass CRLSP backs up the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] display mpls lsp FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE 1.1.1.1/4/61400 RSVP -/1245 Vlan1 2.1.1.2 Local -/- Vlan1 [SwitchB] display mpls lsp FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE 1.1.1.1/4/614000 RSVP 1245/3 Vlan2 Backup 1245/3 Tun5 2.2.2.2/5/30914 RSVP -/1150 Vlan2 3.2.1.2 Local -/- Vlan4 3.1.1.2 Local -/- Vlan2 [SwitchE] display mpls lsp FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE 2.2.2.2/5/30914 RSVP 1150/3 Vlan5 3.3.1.2 Local -/- Vlan5
# Shut down the protected interface VLAN-interface 2 on the PLR (Switch B).
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] shutdown [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel 4 command on Switch A to display information about the primary CRLSP. The output shows that the tunnel interface is still up. (Details not shown.)
# Execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on Switch A to display detailed information about the tunnel interface.
[SwitchA] display mpls te tunnel-interface Tunnel Name : Tunnel 4 Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP being set up) Tunnel Attributes : LSP ID : 18753 Tunnel ID : 4 Admin State : Normal Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 3.3.3.3 Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : - Resv Style : SE Tunnel mode : - Reverse-LSP name : - Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: - Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 0 kbps Reserved Bandwidth : 0 kbps Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7 Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0 Explicit Path : pri-path Backup Explicit Path : - Metric Type : TE Record Route : Disabled Record Label : Disabled FRR Flag : Enabled Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: - Backup Bandwidth : - Route Pinning : Disabled Retry Limit : 10 Retry Interval : 2 sec Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : - Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : - Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : - Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : - Collected Bandwidth : -
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: If you execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command immediately after an FRR, you can see two CRLSPs in up state. This is because FRR uses the make-before-break mechanism to set up a new LSP, and the old LSP is deleted after the new one has been established for a while. | |
# Execute the display mpls lsp command on Switch B. The output shows that the bypass tunnel is in use.
[SwitchB] display mpls lsp FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE 1.1.1.1/4/61400 RSVP 1136/3 Tun5 2.2.2.2/5/30914 RSVP -/1149 Vlan4 3.2.1.2 Local -/- Vlan4
# On the PLR, configure the interval for selecting an optimal bypass tunnel as 5 seconds.
[SwitchB] rsvp [SwitchB-rsvp] fast-reroute timer 5 [SwitchB-rsvp] quit
# On the PLR, bring up the protected interface VLAN-interface 2.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2 [SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] undo shutdown
# On Switch A, execute the display interface tunnel 4 command to display information about the primary CRLSP. The output shows that the tunnel interface is in up state. (Details not shown.)
# Wait for about 5 seconds, execute the display mpls lsp verbose command on Switch B. The output shows that Tunnel 5 is bound to interface VLAN-interface 2 but not in use. (Details not shown.)
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on Switch A. The output shows a static route entry with interface Tunnel4 as the output interface. (Details not shown.)