SSL security services
SSL provides the following security services:
Privacy—SSL uses a symmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt data. It uses the asymmetric key algorithm of RSA to encrypt the key to be used by the symmetric encryption algorithm.
Authentication—SSL supports certificate-based identity authentication of the server and client by using the digital signatures. The SSL server and client obtain certificates from a CA through the PKI.
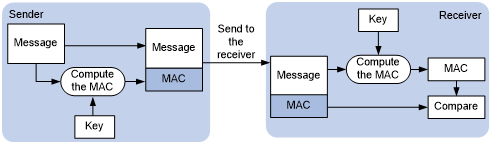
Integrity—SSL uses the message authentication code (MAC) to verify message integrity. It uses a MAC algorithm and a key to transform a message of any length to a fixed-length message. Any change to the original message will result in a change to the calculated fixed-length message. As shown in Figure 105, the message integrity verification process is as follows:
The sender uses a MAC algorithm and a key to calculate a MAC value for a message. Then, it appends the MAC value to the message and sends the message to the receiver.
The receiver uses the same key and MAC algorithm to calculate a MAC value for the received message. It compares the resulting MAC value with the MAC value appended to the message.
If the two MAC values are identical, the receiver considers the message intact. Otherwise, the receiver considers that the message was tampered with and discards the message.
Figure 105: Message integrity verification by a MAC algorithm
For more information about symmetric key algorithms, asymmetric key algorithm RSA and digital signature, see "Managing public keys."
For more information about PKI, certificate, and CA, see "Configuring PKI."