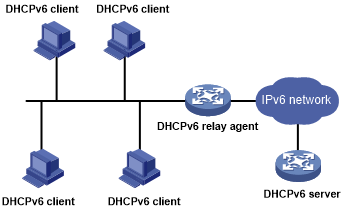
Overview
A DHCPv6 client usually uses a multicast address to contact the DHCPv6 server on the local link to obtain an IPv6 address and other configuration parameters. As shown in Figure 74, if the DHCPv6 server resides on another subnet, the DHCPv6 clients need a DHCPv6 relay agent to contact the server. The relay agent feature avoids deploying a DHCP server on each subnet.
Figure 74: Typical DHCPv6 relay agent application
As shown in Figure 75, a DHCPv6 client obtains an IPv6 address and other network configuration parameters from a DHCPv6 server through a DHCPv6 relay agent. The following example uses rapid assignment to describe the process:
The DHCPv6 client sends a Solicit message containing the Rapid Commit option to the multicast address FF02::1:2 of all the DHCPv6 servers and relay agents.
After receiving the Solicit message, the DHCPv6 relay agent encapsulates the message into the Relay Message option of a Relay-forward message, and sends the message to the DHCPv6 server.
After obtaining the Solicit message from the Relay-forward message, the DHCPv6 server performs the following tasks:
Selects an IPv6 address and other required parameters.
Adds them to a reply that is encapsulated within the Relay Message option of a Relay-reply message.
Sends the Relay-reply message to the DHCPv6 relay agent.
The DHCPv6 relay agent obtains the reply from the Relay-reply message and sends the reply to the DHCPv6 client.
The DHCPv6 client uses the IPv6 address and other network parameters assigned by the DHCPv6 server to complete network configuration.
Figure 75: Operating process of a DHCPv6 relay agent