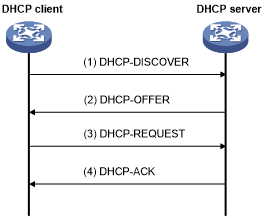
IP address allocation process
Figure 11: IP address allocation process
As shown in Figure 11, a DHCP server assigns an IP address to a DHCP client in the following process:
The client broadcasts a DHCP-DISCOVER message to locate a DHCP server.
Each DHCP server offers configuration parameters such as an IP address to the client in a DHCP-OFFER message. The sending mode of the DHCP-OFFER is determined by the flag field in the DHCP-DISCOVER message. For more information, see "DHCP message format."
If the client receives multiple offers, it accepts the first received offer, and broadcasts it in a DHCP-REQUEST message to formally request the IP address. (IP addresses offered by other DHCP servers can be assigned to other clients.)
All DHCP servers receive the DHCP-REQUEST message. However, only the server selected by the client does one of the following operations:
Returns a DHCP-ACK message to confirm that the IP address has been allocated to the client.
Returns a DHCP-NAK message to deny the IP address allocation.
After receiving the DHCP-ACK message, the client verifies the following details before using the assigned IP address:
The assigned IP address is not in use. To verify this, the client broadcasts a gratuitous ARP packet. The assigned IP address is not in use if no response is received within the specified time.
The assigned IP address is not on the same subnet as any IP address in use on the client.
Otherwise, the client sends a DHCP-DECLINE message to the server to request an IP address again.