LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) provides standard multiplatform directory service. LDAP was developed on the basis of the X.500 protocol. It improves the following functions of X.500:
Read/write interactive access.
Browse.
Search.
LDAP is suitable for storing data that does not often change. The protocol is used to store user information. For example, LDAP server software Active Directory Server is used in Microsoft Windows operating systems. The software stores the user information and user group information for user login authentication and authorization.
LDAP directory service
LDAP uses directories to maintain the organization information, personnel information, and resource information. The directories are organized in a tree structure and include entries. An entry is a set of attributes with distinguished names (DNs). The attributes are used to store information such as usernames, passwords, emails, computer names, and phone numbers.
LDAP uses a client/server model, and all directory information is stored in the LDAP server. Commonly used LDAP server products include Microsoft Active Directory Server, IBM Tivoli Directory Server, and Sun ONE Directory Server.
LDAP authentication and authorization
AAA can use LDAP to provide authentication and authorization services for users. LDAP defines a set of operations to implement its functions. The main operations for authentication and authorization are the bind operation and search operation.
The bind operation allows an LDAP client to perform the following operations:
Establish a connection with the LDAP server.
Obtain the access rights to the LDAP server.
Check the validity of user information.
The search operation constructs search conditions and obtains the directory resource information of the LDAP server.
In LDAP authentication, the client completes the following operations:
Uses the LDAP server administrator DN to bind with the LDAP server. After the binding is created, the client establishes a connection to the server and obtains the right to search.
Constructs search conditions by using the username in the authentication information of a user. The specified root directory of the server is searched and a user DN list is generated.
Binds with the LDAP server by using each user DN and password. If a binding is created, the user is considered legal.
In LDAP authorization, the client performs the same operations as in LDAP authentication. When the client constructs search conditions, it obtains both authorization information and the user DN list.
If the authorization information meets the authorization requirements, the authorization process ends.
If the authorization information does not meet the authorization requirements, the client sends an administrator bind request to the LDAP server. This operation obtains the right to search for authorization information about users on the user DN list.
Basic LDAP packet exchange process
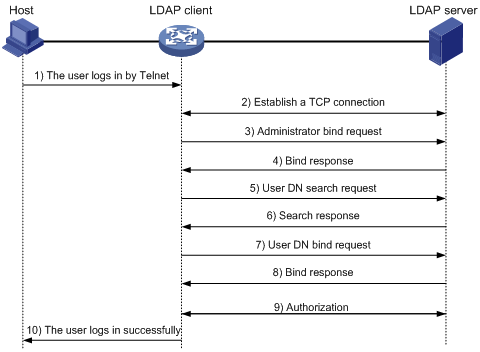
The following example illustrates the basic packet exchange process during LDAP authentication and authorization for a Telnet user.
Figure 7: Basic packet exchange process for LDAP authentication of a Telnet user
The basic packet exchange process is as follows:
A Telnet user initiates a connection request and sends the username and password to the LDAP client.
After receiving the request, the LDAP client establishes a TCP connection with the LDAP server.
To obtain the right to search, the LDAP client uses the administrator DN and password to send an administrator bind request to the LDAP server.
The LDAP server processes the request. If the bind operation is successful, the LDAP server sends an acknowledgment to the LDAP client.
The LDAP client sends a user DN search request with the username of the Telnet user to the LDAP server.
After receiving the request, the LDAP server searches for the user DN by the base DN, search scope, and filtering conditions. If a match is found, the LDAP server sends a response to notify the LDAP client of the successful search. There might be one or more user DNs found.
The LDAP client uses the obtained user DN and the entered user password as parameters to send a user DN bind request to the LDAP server. The server will check whether the user password is correct.
The LDAP server processes the request, and sends a response to notify the LDAP client of the bind operation result. If the bind operation fails, the LDAP client uses another obtained user DN as the parameter to send a user DN bind request to the LDAP server. This process continues until a DN is bound successfully or all DNs fail to be bound. If all user DNs fail to be bound, the LDAP client notifies the user of the login failure and denies the user's access request.
The LDAP client and server perform authorization exchanges. If another scheme (for example, an HWTACACS scheme) is expected for authorization, the LDAP client exchanges authorization packets with the HWTACACS authorization server instead.
After successful authorization, the LDAP client notifies the user of the successful login.