Basic concepts
DHCPv6 multicast address
The multicast address FF05::1:3 identifies all DHCPv6 servers on the site-local network. The multicast address FF02::1:2 identifies all DHCPv6 servers and relay agents on the link-local link.
DUID
A DHCP unique identifier (DUID) uniquely identifies a DHCPv6 switch (DHCPv6 client, server, or relay agent).
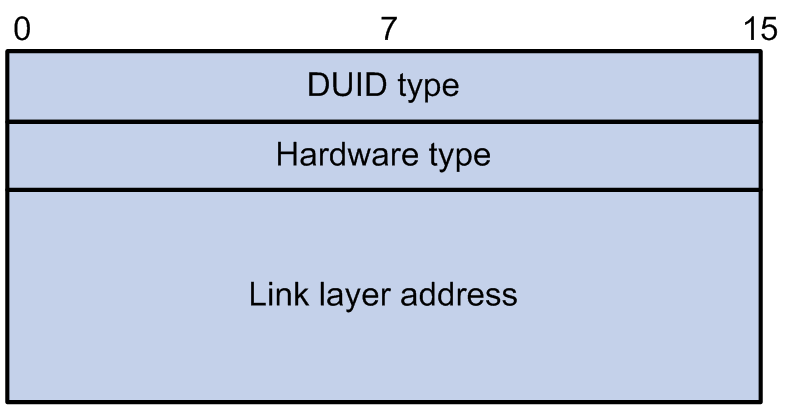
Figure 55: Format of DUID-LL
A DUID based on link-layer address (DUID-LL) defined in RFC 3315 is used to identify a DHCPv6 switch. Figure 55 shows the DUID-LL format, where:
DUID type: The switch supports DUID-LL as the DUID type with the value of 0x0003.
Hardware type: The switch supports Ethernet as the hardware type with the value of 0x0001.
Link layer address: Its value is the bridge MAC address of the switch.
IA
Identified by an IAID, an Identity Association (IA) provides a construct through which the obtained addresses, prefixes, and other configuration parameters assigned from a server to a client are managed. A client can maintain multiple IAs, each of which is configured on an interface to manage the addresses, prefixes, and other configuration parameters obtained by that interface.
IAID
An IAID uniquely identifies an IA. It is chosen by the client and must be unique among the IAIDs on the client.
PD
The Prefix Delegation (PD) is the lease record created by the DHCPv6 server for each assigned prefix. The PD contains information such as the IPv6 prefix, client DUID, IAID, valid lifetime, preferred lifetime, lease expiration time, and the IPv6 address of the requesting client.