The HPE SDN ecosystem
SDN architecture separates the network control plane from the forwarding hardware on network devices. Control can then be centralized, while forwarding remains distributed. SDN is based on OpenFlow, which is a standards-based protocol allowing for a centralized-control plane in a separate device (the controller).
OpenFlow is managed by the Open Networking Foundation (ONF). By separating the control plane from the forwarding plane, SDN makes it possible for the network status and capabilities to be exposed directly to the business service layer, so that business systems can request services from the network directly. SDN applications thus provide higher level application direction to the SDN controller. And freed from the control function, the forwarding plane can then provide optimized packet processing at very high speeds.
The HPE VAN SDN Controller is the central building block of the HPE SDN ecosystem and creates a platform for application development.
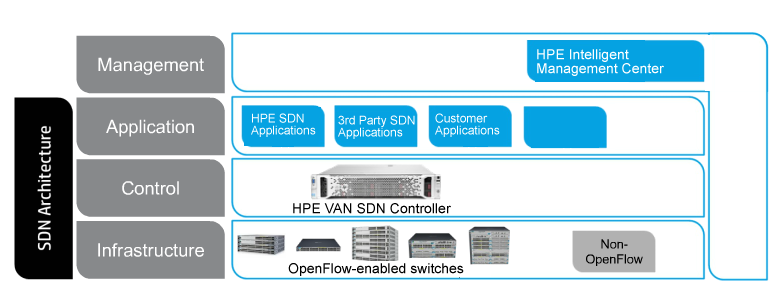
The HPE SDN ecosystem includes the following:
Infrastructure. The infrastructure layer is made up of network devices, typically but not exclusively routers and switches. The devices are OpenFlow-enabled. An OpenFlow switch consists of one or more flow tables and a group table, which perform packet lookups and forwarding and provide an OpenFlow channel to the HPE VAN SDN Controller. The switch communicates with the controller and the controller manages the switch via the OpenFlow protocol. Hewlett Packard Enterprise has more than 50 switch models that are OpenFlow-enabled.
Control. HPE VAN SDN Controller provides centralized control and automation for an SDN network. The controller controls policy and forwarding decisions, which are communicated to the OpenFlow-enabled switches in the data center or campus network. A variety of Hewlett Packard Enterprise and third-party SDN applications can leverage the controller to automatically deliver the necessary business and network service levels.
Applications. Hewlett Packard Enterprise and third-party SDN applications provide a true end-to-end service level for network performance, quality of service, and security, which can be tuned to an applications’ needs. For example, SDN applications can inspect flows, or perform other network control functions via the HPE VAN SDN Controller. Hewlett Packard Enterprise SDN applications include: HPE Network Protector SDN Application, HPE Network Optimizer SDN Application and HPE Network Visualizer SDN Application.
The extensibility and open APIs of the HPE VAN SDN Controller allows new applications to be created that make requests of the underlying network, without the need to physically uproot or re-configure the underlying infrastructure. Northbound APIs utilize the REST architecture and provide easy access to applications that are integrated directly in the controller or off the controller. Native APIs, provided in Java, deliver support to Network Control applications that are integrated directly in the controller.
Management. The HPE Intelligent Management Center (IMC) VAN SDN Manager software integrates with HPE IMC to provide administrators with a single interface to manage both the traditional network and the SDN. The IMC VAN SDN Manager Software monitors and manages all three layers of the SDN architecture: infrastructure, control, and application, providing comprehensive management—including fault, configuration, accounting, monitoring, and security for the controller and OpenFlow infrastructure. IMC provides full controller application life cycle management and monitoring, reporting of network service status and OpenFlow-related information, and SDN network visualization.
In addition, the HPE VAN SDN Controller provides REST and Java APIs that enable applications to interact with the controller to receive alerts, to get information about the network, devices, and controller, and to perform various network management tasks.