Configuring an IPv4 over IPv6 GRE tunnel
Network requirements
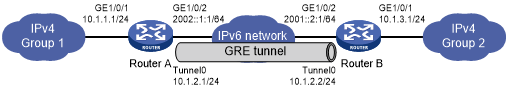
As shown in Figure 140, two IPv4 subnets Group 1 and Group 2 are connected to an IPv6 network. Create a GRE/IPv6 tunnel between Router A and Router B, so the two IPv4 subnets can communicate with each other through the GRE tunnel over the IPv6 network.
Figure 140: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Before performing the following configuration, configure an IP address for each interface, and make sure Router A and Router B can reach each other.
Configure Router A:
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 0, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv6.
<RouterA> system-view [RouterA] interface tunnel 0 mode gre ipv6
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface.
[RouterA-Tunnel0] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
# Configure the source address of the tunnel interface as the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Router A.
[RouterA-Tunnel0] source 2002::1:1
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface as the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Router B.
[RouterA-Tunnel0] destination 2001::2:1 [RouterA-Tunnel0] quit
# Configure a static route from Router A through the tunnel interface to Group 2.
[RouterA] ip route-static 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0
Configure Router B:
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 0, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv6.
<RouterB> system-view [RouterB] interface tunnel 0 mode gre ipv6
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface.
[RouterB-Tunnel0] ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
# Configure the source address of the tunnel interface as the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Router B.
[RouterB-Tunnel0] source 2001::2:1
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface as the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Router A.
[RouterB-Tunnel0] destination 2002::1:1 [RouterB-Tunnel0] quit
# Configure a static route from Router B through the tunnel interface to Group 1.
[RouterB] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0
Verifying the configuration
# Display tunnel interface information on Router A.
[RouterA] display interface tunnel 0
Tunnel0
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: Tunnel0 Interface
Bandwidth: 64kbps
Maximum Transmit Unit: 1456
Internet Address is 10.1.2.1/24 Primary
Tunnel source 2002::1:1, destination 2001::2:1
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IPv6
GRE key disabled
Checksumming of GRE packets disabled
Output queue - Urgent queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/100/0
Output queue - Protocol queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/500/0
Output queue - FIFO queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/75/0
Last clearing of counters: Never
Last 300 seconds input rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
Output: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
# Display tunnel interface information on Router B.
[RouterB] display interface tunnel 0
Tunnel0
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: Tunnel0 Interface
Bandwidth: 64kbps
Maximum Transmit Unit: 1456
Internet Address is 10.1.2.2/24 Primary
Tunnel source 2002::2:1, destination 2001::1:1
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IPv6
GRE key disabled
Checksumming of GRE packets disabled
Output queue - Urgent queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/100/0
Output queue - Protocol queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/500/0
Output queue - FIFO queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/75/0
Last clearing of counters: Never
Last 300 seconds input rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
Output: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 drops
# From Router B, ping the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on Router A.
[RouterB] ping -a 10.1.3.1 10.1.1.1 Ping 10.1.1.1 (10.1.1.1) from 10.1.3.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break 56 bytes from 10.1.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms 56 bytes from 10.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 10.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms 56 bytes from 10.1.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=0.000 ms 56 bytes from 10.1.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms --- Ping statistics for 10.1.1.1 --- 5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.000/1.000/2.000/0.632 ms
The output shows that Router B can successfully ping Router A.