Prefix translation
NAT64 prefix translation
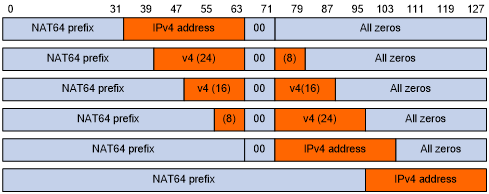
NAT64 prefix is an IPv6 address prefix used to construct an IPv6 address representing an IPv4 node in an IPv6 network. The IPv6 hosts do not use a constructed IPv6 address as their real IP address. The length of a NAT64 prefix can be 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, or 96.
As shown in Figure 106, the construction methods vary depending on the NAT64 prefix length. Bits 64 through 71 in the constructed IPv6 address are reserved bits and must always be zero.
If the prefix length is 32, 64, or 96 bits, the IPv4 address contained in the IPv6 address will be integral.
If the prefix length is 40, 48, or 56 bits, the IPv4 address contained in the IPv6 address will be divided into two parts by bits 64 through 71.
Figure 106: IPv6 address construction with NAT 64 prefix and IPv4 address
AFT uses a NAT64 prefix to perform the following translation:
IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation. AFT translates a source IPv4 address to an IPv6 address that is created by using the NAT64 prefix and the IPv4 address.
IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation. AFT uses the NAT64 prefix to match destination IPv6 addresses and extracts the embedded IPv4 address from matching IPv6 addresses.
A NAT64 prefix cannot be on the same subnet as any interface on the device.
IVI prefix translation
An IVI prefix is a 32-bit IPv6 address prefix. An IVI address is the IPv6 address that an IPv6 node uses. As shown in Figure 107, the IVI address includes an IVI prefix and an IPv4 address.
Figure 107: IVI address format
AFT uses an IVI prefix for IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation. If a source IPv6 address matches the IVI prefix, AFT translates it to the embedded IPv4 address.
General prefix translation
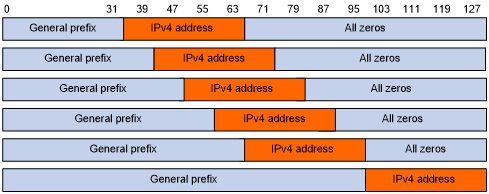
A general prefix is an IPv6 address prefix used to construct an IPv6 address representing an IPv4 node in an IPv6 network. The length of a general prefix can be 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, or 96.
As shown in Figure 108, a general prefix based IPv6 address does not have reserved bits, and an IPv4 address is embedded as a whole into an IPv6 address.
Figure 108: General prefix based IPv6 address format
AFT uses a general prefix for IPv6-to-IPv4 source and destination address translation. If a source or destination IPv6 address matches the general prefix, AFT translates it to the embedded IPv4 address.
A general prefix cannot be on the same subnet as any interface on the device.