Transparent DNS proxy on the LB device
The LB device distributes DNS requests to multiple links by changing the destination IP address of DNS requests.
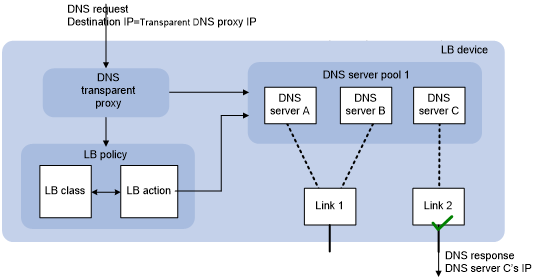
As shown in Figure 58, the LB device contains the following elements:
Transparent DNS proxy—The LB device performs transparent DNS proxy for a DNS request only when the port number of the DNS request matches the port number of the transparent DNS proxy.
DNS server pool—A group of DNS servers.
DNS server—Entity that processes DNS requests.
Link—Physical link provided by an ISP.
LB class—Classifies packets to implement load balancing based on packet type.
LB action—Drops, forwards, or modifies packets.
LB policy—Associates an LB class with an LB action. An LB policy can be referenced by the transparent DNS proxy.
Figure 58: Transparent DNS proxy on the LB device
If the destination IP address and port number of a DNS request match those of the transparent DNS proxy, the LB device processes the DNS request as follows:
The LB device finds the DNS server pool associated with the transparent DNS proxy.
The LB device selects a DNS server according to the scheduling algorithm configured for the DNS server pool.
The LB device uses the IP address of the selected DNS server as the destination IP address of the DNS request, and sends the request to the DNS server.
The DNS server receives and processes the DNS request, and replies with a DNS response.
The intranet user can now access the external server after receiving the DNS response.