VRRP-Track-NQA collaboration configuration example
Network requirements
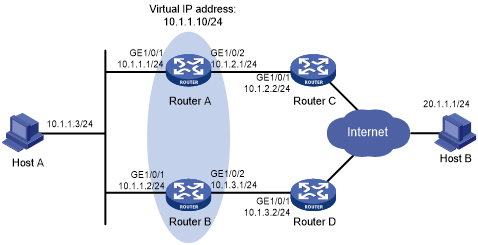
As shown in Figure 35:
Host A requires access to Host B. The default gateway of Host A is 10.1.1.10/24.
Router A and Router B belong to VRRP group 1. The virtual IP address of VRRP group 1 is 10.1.1.10.
Configure VRRP-Track-NQA collaboration to monitor the uplink on the master and meet the following requirements:
When Router A operates correctly, it forwards packets from Host A to Host B.
When NQA detects a fault on the uplink of Router A, Router B forwards packets from Host A to Host B.
Figure 35: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Configure the IP address of each interface, as shown in Figure 35. (Details not shown.)
Configure an NQA operation on Router A:
# Create an NQA operation with administrator name admin and operation tag test.
<RouterA> system-view [RouterA] nqa entry admin test
# Specify the ICMP echo operation type.
[RouterA-nqa-admin-test] type icmp-echo
# Specify 10.1.2.2 as the destination address of ICMP echo requests.
[RouterA-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] destination ip 10.1.2.2
# Configure the ICMP echo operation to repeat every 100 milliseconds.
[RouterA-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] frequency 100
# Create reaction entry 1, specifying that five consecutive probe failures trigger the Track module.
[RouterA-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] reaction 1 checked-element probe-fail threshold-type consecutive 5 action-type trigger-only [RouterA-nqa-admin-test-icmp-echo] quit
# Start the NQA operation.
[RouterA] nqa schedule admin test start-time now lifetime forever
On Router A, configure track entry 1, and associate it with reaction entry 1 of the NQA operation.
[RouterA] track 1 nqa entry admin test reaction 1 [RouterA-track-1] quit
Configure VRRP on Router A:
# Specify VRRPv2 to run on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp version 2
# Create VRRP group 1, and configure virtual IP address 10.1.1.10 for the group.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.10
# Set the priority of Router A to 110 in VRRP group 1.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 priority 110
# Set the authentication mode of VRRP group 1 to simple, and the authentication key to hello.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 authentication-mode simple plain hello
# Configure the master to send VRRP packets every 500 centiseconds.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 timer advertise 500
# Configure Router A to operate in preemptive mode and set the preemption delay to 5000 centiseconds.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 5000
# Associate VRRP group 1 with track entry 1 and decrease the router priority by 30 when the state of track entry 1 changes to negative.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 track 1 priority reduced 30
Configure VRRP on Router B:
# Specify VRRPv2 to run on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view [RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp version 2
# Create VRRP group 1, and configure virtual IP address 10.1.1.10 for the group.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.10
# Set the authentication mode of VRRP group 1 to simple, and the authentication key to hello.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 authentication-mode simple plain hello
# Configure the master to send VRRP packets every 500 centiseconds.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 timer advertise 500
# Configure Router B to operate in preemptive mode and set the preemption delay to 5000 centiseconds.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode delay 5000
Verifying the configuration
# Ping Host B from Host A to verify that Host B is reachable. (Details not shown.)
# Display detailed information about VRRP group 1 on Router A.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display vrrp verbose
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running Mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 500
Admin Status : Up State : Master
Config Pri : 110 Running Pri : 110
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5000
Auth Type : Simple Key : ******
Virtual IP : 10.1.1.10
Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0101
Master IP : 10.1.1.1
VRRP Track Information:
Track Object : 1 State : Positive Pri Reduced : 30
# Display detailed information about VRRP group 1 on Router B.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display vrrp verbose
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running Mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 500
Admin Status : Up State : Backup
Config Pri : 100 Running Pri : 100
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5000
Become Master : 2200ms left
Auth Type : Simple Key : ******
Virtual IP : 10.1.1.10
Master IP : 10.1.1.1
The output shows that in VRRP group 1, Router A is the master and Router B is a backup. Router A forwards packets from Host A to Host B.
# Disconnect the link between Router A and Router C, and verify that Host A can still ping Host B. (Details not shown.)
# Display detailed information about VRRP group 1 on Router A.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display vrrp verbose
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running Mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 500
Admin Status : Up State : Backup
Config Pri : 110 Running Pri : 80
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5000
Become Master : 2200ms left
Auth Type : Simple Key : ******
Virtual IP : 10.1.1.10
Master IP : 10.1.1.2
VRRP Track Information:
Track Object : 1 State : Negative Pri Reduced : 30
# Display detailed information about VRRP group 1 on Router B when a fault is on the link between Router A and Router C.
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display vrrp verbose
IPv4 Virtual Router Information:
Running Mode : Standard
Total number of virtual routers : 1
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 500
Admin Status : Up State : Master
Config Pri : 100 Running Pri : 100
Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 5000
Auth Type : Simple Key : ******
Virtual IP : 10.1.1.10
Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0101
Master IP : 10.1.1.2
The output shows that Router A becomes the backup, and Router B becomes the master. Router B forwards packets from Host A to Host B.