Strict active/standby interface backup with the Track module configuration example
Network requirements
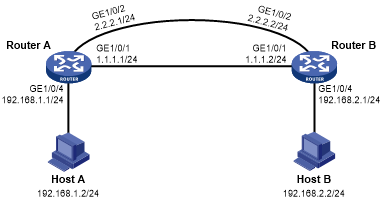
As shown in Figure 4, configure a track entry to monitor the link state of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. When the link of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 fails, the backup interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 comes up to take over.
Figure 4: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Assign IP addresses to interfaces, as shown in Figure 4. (Details not shown.)
Configure routes:
# On Router A, configure static routes to 192.168.2.0/24 through the primary and backup interfaces.
<RouterA> system-view [RouterA] ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 gigabitethernet 1/0/1 1.1.1.2 [RouterA] ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 2.2.2.2
# On Router B, configure static routes to 192.168.1.0/24.
<RouterB> system-view [RouterB] ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 gigabitethernet 1/0/1 1.1.1.1 [RouterB] ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 2.2.2.1
On Router A, configure track settings:
# Configure track entry 1 to monitor the link state of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[RouterA] track 1 interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Associate track entry 1 with the backup interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] backup track 1 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the backup interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 is in STANDBY state while the primary link is operating correctly.
[RouterA] display interface-backup state IB Track Information: GE1/0/2 Track: 1 State: STANDBY
# Shut down the primary interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] shutdown
# Verify that the backup interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 comes up after the primary link goes down.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display interface-backup state IB Track Information: GE1/0/2 Track: 1 State: UP