Configuration example for NAS-initiated L2TP tunnel
Network requirements
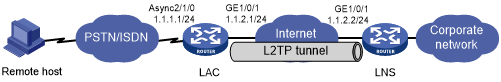
As shown in Figure 30, a PPP user is connected to an LNS through an LAC.
Set up an L2TP tunnel between the LAC and LNS to allow the PPP user to access the corporate network.
Figure 30: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Configure the LAC:
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Create a local user named vpdnuser, set the password, and enable the PPP service.
<LAC> system-view [LAC] local-user vpdnuser class network [LAC-luser-network-vpdnuser] password simple Hello [LAC-luser-network-vpdnuser] service-type ppp [LAC-luser-network-vpdnuser] quit
# Configure local authentication for PPP users in ISP domain system.
[LAC] domain system [LAC-isp-system] authentication ppp local [LAC-isp-system] quit
# Configure CHAP authentication on Async 2/1/0.
[LAC] interface async 2/1/0 [LAC-Async2/1/0] ppp authentication-mode chap [LAC-Async2/1/0] quit
# Enable L2TP.
[LAC] l2tp enable
# Create L2TP group 1 in LAC mode.
[LAC] l2tp-group 1 mode lac
# Configure the local tunnel name as LAC.
[LAC-l2tp1] tunnel name LAC
# Specify PPP user vpdnuser as the condition for the LAC to initiate tunneling requests.
[LAC-l2tp1] user fullusername vpdnuser
# Specify the LNS IP address as 1.1.2.2.
[LAC-l2tp1] lns-ip 1.1.2.2
# Enable tunnel authentication, and specify the tunnel authentication key as aabbcc.
[LAC-l2tp1] tunnel authentication [LAC-l2tp1] tunnel password simple aabbcc [LAC-l2tp1] quit
Configure the LNS:
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Create a local user named vpdnuser, set the password, and enable the PPP service.
<LNS> system-view [LNS] local-user vpdnuser class network [LNS-luser-network-vpdnuser] password simple Hello [LNS-luser-network-vpdnuser] service-type ppp [LNS-luser-network-vpdnuser] quit
# Configure local authentication for PPP users in ISP domain system.
[LNS] domain system [LNS-isp-system] authentication ppp local [LNS-isp-system] quit
# Enable L2TP.
[LNS] l2tp enable
# Create a PPP address pool.
[LNS] ip pool aaa 192.168.0.10 192.168.0.20 [LNS] ip pool aaa gateway 192.168.0.1
# Create Virtual-Template 1, specify its PPP authentication mode as CHAP, and use address pool aaa to assign IP addresses to the PPP users.
[LNS] interface virtual-template 1 [LNS-virtual-template1] ppp authentication-mode chap domain system [LNS-virtual-template1] remote address pool aaa [LNS-virtual-template1] quit
# Create L2TP group 1 in LNS mode.
[LNS] l2tp-group 1 mode lns
# Configure the local tunnel name as LNS.
[LNS-l2tp1] tunnel name LNS
# Specify Virtual-Template 1 for receiving calls from an LAC.
[LNS-l2tp1] allow l2tp virtual-template 1 remote LAC
# Enable tunnel authentication, and specify the tunnel authentication key as aabbcc.
[LNS-l2tp1] tunnel authentication [LNS-l2tp1] tunnel password simple aabbcc [LNS-l2tp1] quit
On the remote system, enter vpdnuser as the username and Hello as the password in the dial-up network window to dial a connection.
Verifying the configuration
After the dial-up connection is established, the remote system can obtain an IP address and can ping the private IP address of the LNS.
# On the LNS, use the display l2tp tunnel command to check the established L2TP tunnels.
[LNS] display l2tp tunnel LocalTID RemoteTID State Sessions RemoteAddress RemotePort RemoteName 196 3542 Established 1 1.1.2.1 1701 LAC
# On the LNS, use the display l2tp session command to check the established L2TP sessions.
[LNS] display l2tp session LocalSID RemoteSID LocalTID State 2041 64 196 Established