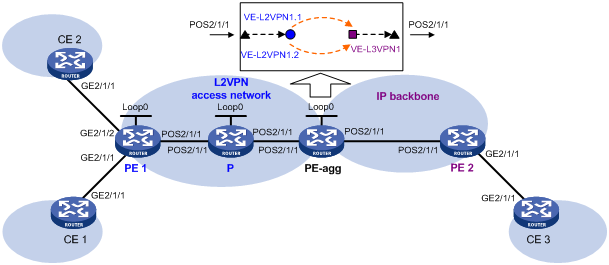
LDP PW access to IP backbone through L2VE subinterfaces
Network requirements
Create LDP PWs between PE 1 and PE-agg on the L2VPN access network, so that CE 1 and CE 2 can access the IP backbone through the PWs.
Configure L2VPN access to the IP backbone through L2VE subinterfaces.
Configure OSPF process 2 to advertise routing information on the IP backbone.
Figure 133: Network diagram
Table 48: Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CE 1 | GE2/1/1 | 100.1.1.1/24 | CE 2 | GE 2/1/1 | 100.1.1.2/24 |
PE 1 | Loop0 | 1.1.1.9/32 | PE-agg | Loop0 | 3.3.3.9/32 |
POS2/1/0 | 10.2.1.1/24 | POS2/1/0 | 10.2.2.2/24 | ||
P | Loop0 | 2.2.2.9/32 | POS2/1/1 | 10.3.3.1/24 | |
POS2/1/0 | 10.2.1.2/24 | VE-L3VPN1 | 100.1.1.3/24 | ||
POS2/1/1 | 10.2.2.1/24 | PE 2 | POS2/1/0 | 10.3.3.2/24 | |
CE 3 | GE2/1/1 | 100.2.1.2/24 | GE2/1/1 | 100.2.1.1/24 |
Configuration procedure
Configure IP addresses for interfaces as shown in Table 48. (Details not shown.)
Create interfaces VE-L2VPN 1 and VE-L3VPN 1 on PE-agg:
# Create interface VE-L2VPN 1, subinterface VE-L2VPN 1.1, and subinterface VE-L2VPN 1.2.
<PEagg> system-view [PEagg] interface ve-l2vpn 1 [PEagg-VE-L2VPN1] quit [PEagg] interface ve-l2vpn 1.1 [PEagg-VE-L2VPN1.1] quit [PEagg] interface ve-l2vpn 1.2 [PEagg-VE-L2VPN1.2] quit
# Create interface VE-L3VPN 1, and configure an IP address for the interface.
[PEagg] interface ve-l3vpn 1 [PEagg-VE-L3VPN1] ip address 100.1.1.3 24 [PEagg-VE-L3VPN1] quit
Configure MPLS L2VPN:
Configure OSPF on PE 1, P, and PE-agg, and advertise interface addresses:
# Configure PE 1.
<PE1> system-view [PE1] ospf [PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure the P device.
<P> system-view [P] ospf [P-ospf-1] area 0 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [P-ospf-1] quit
# Configure PE-agg.
[PEagg] ospf [PEagg-ospf-1] area 0 [PEagg-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 [PEagg-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 [PEagg-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PEagg-ospf-1] quit
Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP on PE 1, P, and PE-agg:
# Configure PE 1.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [PE1] mpls ldp [PE1-ldp] lsp-trigger all [PE1-ldp] quit [PE1] interface pos 2/1/0 [PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [PE1-Pos2/1/0] quit
# Configure the P device.
[P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [P] mpls ldp [P-ldp] lsp-trigger all [P-ldp] quit [P] interface pos 2/1/0 [P-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [P-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [P-Pos2/1/0] quit [P] interface pos 2/1/1 [P-Pos2/1/1] mpls enable [P-Pos2/1/1] mpls ldp enable [P-Pos2/1/1] quit
# Configure PE-agg.
[PEagg] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [PEagg] mpls ldp [PEagg-ldp] lsp-trigger all [PEagg-ldp] quit [PEagg] interface pos 2/1/0 [PEagg-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [PEagg-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [PEagg-Pos2/1/0] quit
Enable L2VPN on PE 1 and PE-agg:
# Configure PE 1.
[PE1] l2vpn enable
# Configure PE-agg.
[PEagg] l2vpn enable
Create cross-connect groups on PE 1 and PE-agg:
# On PE-agg, create a cross-connect group named vpna, create a cross-connect named ldp in the group, and bind subinterface VE-L2VPN 1.1 to the cross-connect.
[PEagg] xconnect-group vpna [PEagg-xcg-vpna] connection ldp [PEagg-xcg-vpna-ldp] ac interface ve-l2vpn 1.1
# On PE-agg, create an LDP PW for the cross-connect to bind the AC to the PW.
[PEagg-xcg-vpna-ldp] peer 1.1.1.9 pw-id 500 [PEagg-xcg-vpna-ldp-1.1.1.9-500] quit [PEagg-xcg-vpna-ldp] quit [PEagg-xcg-vpna] quit
# On PE-agg, create a cross-connect group named vpnb, create a cross-connect named ldp in the group, and bind subinterface VE-L2VPN 1.2 to the cross-connect.
[PEagg] xconnect-group vpnb [PEagg-xcg-vpnb] connection ldp [PEagg-xcg-vpnb-ldp] ac interface ve-l2vpn 1.2
# On PE-agg, create an LDP PW for the cross-connect to bind the AC to the PW.
[PEagg-xcg-vpnb-ldp] peer 1.1.1.9 pw-id 501 [PEagg-xcg-vpnb-ldp-1.1.1.9-501] quit [PEagg-xcg-vpnb-ldp] quit [PEagg-xcg-vpnb] quit
# On PE 1, create a cross-connect group named vpna, create a cross-connect named ldp in the group, and bind GigabitEthernet 2/1/1 to the cross-connect.
[PE1] xconnect-group vpna [PE1-xcg-vpna] connection ldp [PE1-xcg-vpna-ldp] ac interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1
# On PE 1, create an LDP PW for the cross-connect to bind the AC to the PW.
[PE1-xcg-vpna-ldp] peer 3.3.3.9 pw-id 500 [PE1-xcg-vpna-ldp-3.3.3.9-500] quit [PE1-xcg-vpna-ldp] quit [PE1-xcg-vpna] quit
# On PE 1, create a cross-connect group named vpnb, create a cross-connect named ldp in the group, and bind GigabitEthernet 2/1/2 to the cross-connect.
[PE1]xconnect-group vpnb [PE1-xcg-vpnb]connection ldp [PE1-xcg-vpnb-ldp] ac interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2
# On PE 1, create an LDP PW for the cross-connect to bind the AC to the PW.
[PE1-xcg-vpnb-ldp] peer 3.3.3.9 pw-id 501 [PE1-xcg-vpnb-ldp-3.3.3.9-500] quit [PE1-xcg-vpnb-ldp] quit [PE1-xcg-vpnb] quit
Configure OSPF process 2 to advertise routing information on the IP backbone:
# Configure CE 1.
[CE1] ospf 2 [CE1-ospf-2] area 0 [CE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [CE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit [CE1-ospf-2] quit
# Configure PE-agg.
[PEagg] ospf 2 [PEagg-ospf-2] area 0 [PEagg-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [PEagg-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 [PEagg-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PEagg-ospf-2] quit
# Configure PE 2.
<PE2> system-view [PE2] ospf 2 [PE2-ospf-2] area 0 [PE2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [PE2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 [PE2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PE2-ospf-2] quit
# Configure CE 2.
<CE2> system-view [CE2] ospf 2 [CE2-ospf-2] area 0 [CE2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 100.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [CE2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit [CE2-ospf-2] quit
The default MTU value varies by interface type. To avoid packet fragmentation, set the MTU value for each POS interface on each device to 1500 bytes. The following shows the MTU configuration on PE 1.
[PE1] int pos 2/1/0 [PE1-Pos2/1/0] mtu 1500 [PE1-Pos2/1/0] shutdown [PE1-Pos2/1/0] undo shutdown
Verifying the configuration
# Ping CE 3 from CE 1 and CE 2 to verify the connectivity. This example uses CE 1.
<CE1> ping 100.2.1.2 Ping 100.2.1.2 (100.2.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break 56 bytes from 100.2.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=128 time=1.073 ms 56 bytes from 100.2.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=1.428 ms 56 bytes from 100.2.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=19.367 ms 56 bytes from 100.2.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=1.013 ms 56 bytes from 100.2.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=0.684 ms --- Ping statistics for 100.2.1.2 --- 5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.684/4.713/19.367/7.331 ms