Configuring IPv6 MPLS L3VPN inter-AS option A
Network requirements
CE 1 and CE 2 belong to the same VPN. CE 1 accesses the network through PE 1 in AS 100 and CE 2 accesses the network through PE 2 in AS 200.
Configure IPv6 MPLS L3VPN inter-AS option A, and use VRF-to-VRF method to manage VPN routes.
Run OSPF on the MPLS backbone of each AS.
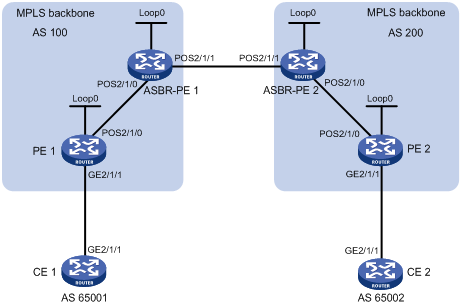
Figure 92: Network diagram
Table 31: Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CE 1 | GE2/1/1 | 2001:1::1/96 | CE 2 | GE2/1/1 | 2001:2::1/96 |
PE 1 | Loop0 | 1.1.1.9/32 | PE 2 | Loop0 | 4.4.4.9/32 |
GE2/1/1 | 2001:1::2/96 | GE2/1/1 | 2001:2::2/96 | ||
POS2/1/0 | 172.1.1.2/24 | POS2/1/0 | 162.1.1.2/24 | ||
ASBR-PE1 | Loop0 | 2.2.2.9/32 | ASBR-PE2 | Loop0 | 3.3.3.9/32 |
POS2/1/0 | 172.1.1.1/24 | POS2/1/0 | 162.1.1.1/24 | ||
POS2/1/1 | 2002:1::1/96 | POS2/1/1 | 2002:1::2/96 |
Configuration procedure
Configure an IGP on each MPLS backbone to ensure IP connectivity within the backbone.
This example uses OSPF. Be sure to advertise the route to the 32-bit loopback interface address of each router through OSPF. Use the loopback interface address of a router as the router's LSR ID. (Details not shown.)
# Execute the display ospf peer command to verify that each ASBR-PE has established an OSPF adjacency in Full state with the PE in the same AS, and that the PEs and ASBR-PEs in the same AS have learned the routes to the loopback interfaces of each other. Execute the ping command to verify that the PEs and ASBR-PEs in the same AS can ping each other. (Details not shown.)
Configure basic MPLS and enable MPLS LDP on each MPLS backbone to establish LDP LSPs:
# Configure basic MPLS on PE 1, and enable MPLS LDP for both PE 1 and the interface connected to ASBR-PE 1.
<PE1> system-view [PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [PE1] mpls ldp [PE1-ldp] quit [PE1] interface pos 2/1/0 [PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [PE1-Pos2/1/0] quit
# Configure basic MPLS on ASBR-PE 1, and enable MPLS LDP for both ASBR-PE 1 and the interface connected to PE 1.
<ASBR-PE1> system-view [ASBR-PE1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [ASBR-PE1] mpls ldp [ASBR-PE1-ldp] quit [ASBR-PE1] interface pos 2/1/0 [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/0] quit
# Configure basic MPLS on ASBR-PE 2, and enable MPLS LDP for both ASBR-PE 2 and the interface connected to PE 2.
<ASBR-PE2> system-view [ASBR-PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [ASBR-PE2] mpls ldp [ASBR-PE2-ldp] quit [ASBR-PE2] interface pos 2/1/0 [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/0] quit
# Configure basic MPLS on PE 2, and enable MPLS LDP for both PE 2 and the interface connected to ASBR-PE 2.
<PE2> system-view [PE2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [PE2] mpls ldp [PE2-ldp] quit [PE2] interface pos 2/1/0 [PE2-Pos2/1/0] mpls enable [PE2-Pos2/1/0] mpls ldp enable [PE2-Pos2/1/0] quit
# Execute the display mpls ldp session command on the routers to verify that the session status is Operational, and that each PE and the ASBR-PE in the same AS have established an LDP neighbor relationship. (Details not shown.)
Configure a VPN instance on the PEs:
For the same VPN, the route targets for the VPN instance on the PE must match those for the VPN instance on the ASBR-PE in the same AS. This is not required for PEs in different ASs.
# Configure CE 1.
<CE1> system-view [CE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ipv6 address 2001:1::1 96 [CE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure PE 1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [PE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [PE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [PE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ipv6 address 2001:1::2 96 [PE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure CE 2.
<CE2> system-view [CE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ipv6 address 2001:2::1 96 [CE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure PE 2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 200:1 both [PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [PE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [PE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [PE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ipv6 address 2001:2::2 96 [PE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# On ASBR-PE 1, create a VPN instance, and bind the VPN instance to the interface connected to ASBR-PE 2. ASBR-PE 1 considers ASBR-PE 2 to be its attached CE.
[ASBR-PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE1-vpn-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [ASBR-PE1-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [ASBR-PE1-vpn-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE1] interface pos 2/1/1 [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/1] ipv6 address 2002:1::1 96 [ASBR-PE1-Pos2/1/1] quit
# On ASBR-PE 2, create a VPN instance, and bind the VPN instance to the interface connected to ASBR-PE 1. ASBR-PE 2 considers ASBR-PE 1 to be its attached CE.
[ASBR-PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE2-vpn-vpn1] route-distinguisher 200:1 [ASBR-PE2-vpn-vpn1] vpn-target 200:1 both [ASBR-PE2-vpn-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE2] interface pos 2/1/1 [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/1] ipv6 address 2002:1::2 96 [ASBR-PE2-Pos2/1/1] quit
# Execute the display ip vpn-instance command to display VPN instance information. Verify that each PE can ping its attached CE, and that ASBR-PE 1 and ASBR-PE 2 can ping each other. (Details not shown.)
Establish EBGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs to allow them to exchange VPN routes:
# Configure CE 1.
[CE1] bgp 65001 [CE1-bgp-default] peer 2001:1::2 as-number 100 [CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast [CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2001:1::2 enable [CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct [CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit [CE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure PE 1.
[PE1] bgp 100 [PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 2001:1::1 as-number 65001 [PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast [PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2001:1::1 enable [PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit [PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure CE 2.
[CE2] bgp 65002 [CE2-bgp-default] peer 2001:2::2 as-number 200 [CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 [CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2001:2::2 enable [CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct [CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit [CE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure PE 2.
[PE2] bgp 200 [PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 2001:2::1 as-number 65002 [PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast [PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2001:2::1 enable [PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit [PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [PE2-bgp-default] quit
Establish an IBGP peer relationship between each PE and the ASBR-PE in the same AS and an EBGP peer relationship between the ASBR-PEs:
# Configure PE 1.
[PE1] bgp 100 [PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6 [PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit [PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure ASBR-PE 1.
[ASBR-PE1] bgp 100 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 2002:1::2 as-number 200 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2002:1::2 enable [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6 [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit [ASBR-PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure ASBR-PE 2.
[ASBR-PE2] bgp 200 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 2002:1::1 as-number 100 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv6 unicast [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] peer 2002:1::1 enable [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 200 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6 [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 4.4.4.9 enable [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit [ASBR-PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure PE 2.
[PE2] bgp 200 [PE2-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 200 [PE2-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6 [PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit [PE2-bgp-default] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the CEs can learn the route to each other and can ping each other. (Details not shown.)