Configuring MPLS L3VPN FRR through VPNv4 route backup for a VPNv4 route
Network requirements
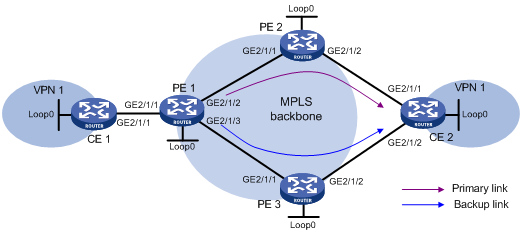
CE 1 and CE 2 belong to VPN 1.
Configure EBGP between CEs and PEs to exchange VPN routes.
Configure OSPF to ensure connectivity between PEs, and configure MP-IBGP to exchange VPNv4 routing information between PEs.
Configure MPLS L3VPN FRR on PE 1 to achieve the following purposes:
When the link PE 1—PE 2 operates correctly, traffic from CE 1 to CE 2 goes through the path CE 1—PE 1—PE 2—CE 2.
When BFD detects that the LSP between PE 1 and PE 2 fails, traffic from CE 1 to CE 2 goes through the path CE 1—PE 1—PE 3—CE 2.
Figure 85: Network diagram
Table 26: Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CE 1 | Loop0 | 5.5.5.5/32 | PE 1 | Loop0 | 1.1.1.1/32 |
GE2/1/1 | 10.2.1.1/24 | GE2/1/1 | 10.2.1.2/24 | ||
PE 2 | Loop0 | 2.2.2.2/32 | GE2/1/2 | 172.1.1.1/24 | |
GE2/1/1 | 172.1.1.2/24 | GE2/1/3 | 172.2.1.1/24 | ||
GE2/1/2 | 10.1.1.2/24 | CE 2 | Loop0 | 4.4.4.4/32 | |
PE 3 | Loop0 | 3.3.3.3/32 | GE2/1/1 | 10.1.1.1/24 | |
GE2/1/1 | 172.2.1.3/24 | GE2/1/2 | 10.3.1.1/24 | ||
GE2/1/2 | 10.3.1.2/24 |
Configuration procedure
Configure IP addresses and masks for interfaces as shown in Table 26, and configure BGP and MPLS L3VPN. (Details not shown.)
For more information about configuring basic MPLS L3VPN, see "Configuring basic MPLS L3VPN."
Configure MPLS L3VPN FRR on PE 1:
# Configure BFD to test the connectivity of the LSP to 2.2.2.2/32.
<PE1> system-view [PE1] mpls bfd enable [PE1] mpls bfd 2.2.2.2 32
# Create routing policy frr, and specify the backup next hop as 3.3.3.3 for the route to 4.4.4.4/32.
[PE1] ip prefix-list abc index 10 permit 4.4.4.4 32 [PE1] route-policy frr permit node 10 [PE1-route-policy] if-match ip address prefix-list abc [PE1-route-policy] apply fast-reroute backup-nexthop 3.3.3.3 [PE1-route-policy] quit
# Configure FRR for VPN instance vpn1 to use routing policy frr.
[PE1] bgp 100 [PE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast [PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] fast-reroute route-policy frr [PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit [PE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Specify the preferred value as 100 for routes received from PE 2. This value is greater than the preferred value (0) for routes from PE 3, so PE 1 prefers the routes from PE 2.
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.2 preferred-value 100 [PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit [PE1-bgp-default] quit
Enable MPLS BFD on PE 2.
<PE2> system-view [PE2] mpls bfd enable
Verifying the configuration
# Display detailed information about the route to 4.4.4.4/32 on PE 1. The output shows the backup next hop for the route.
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 4.4.4.4 32 verbose
Summary Count : 1
Destination: 4.4.4.4/32
Protocol: BGP instance default
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h00m03s
Cost: 0 Preference: 255
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x102 OrigAs: 300
NibID: 0x15000002 LastAs: 300
AttrID: 0x2 Neighbor: 2.2.2.2
Flags: 0x110060 OrigNextHop: 2.2.2.2
Label: 1146 RealNextHop: 172.1.1.2
BkLabel: 1275 BkNextHop: 172.2.1.3
Tunnel ID: Invalid Interface: GE2/1/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkInterface: GE2/1/3
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A