Configuring HoVPN
Network requirements
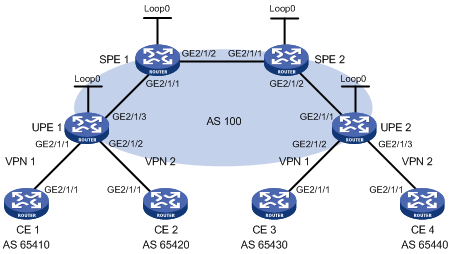
As shown in Figure 81, there are two levels of networks: the backbone and the MPLS VPN networks.
SPEs act as PEs to allow MPLS VPNs to access the backbone.
UPEs act as PEs of the MPLS VPNs to allow end users to access the VPNs.
Performance requirements for the UPEs are lower than those for the SPEs.
SPEs advertise routes permitted by routing policies to UPEs, permitting CE 1 and CE 3 in VPN 1 to communicate with each other and forbidding CE 2 and CE 4 in VPN 2 from communicating with each other.
Figure 81: Network diagram
Table 22: Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CE 1 | GE2/1/1 | 10.2.1.1/24 | CE 3 | GE2/1/1 | 10.1.1.1/24 |
CE 2 | GE2/1/1 | 10.4.1.1/24 | CE 4 | GE2/1/1 | 10.3.1.1/24 |
UPE 1 | Loop0 | 1.1.1.9/32 | UPE 2 | Loop0 | 4.4.4.9/32 |
GE2/1/1 | 10.2.1.2/24 | GE2/1/1 | 172.2.1.1/24 | ||
GE2/1/2 | 10.4.1.2/24 | GE2/1/2 | 10.1.1.2/24 | ||
GE2/1/3 | 172.1.1.1/24 | GE2/1/3 | 10.3.1.2/24 | ||
SPE 1 | Loop0 | 2.2.2.9/32 | SPE 2 | Loop0 | 3.3.3.9/32 |
GE2/1/1 | 172.1.1.2/24 | GE2/1/1 | 180.1.1.2/24 | ||
GE2/1/2 | 180.1.1.1/24 | GE2/1/2 | 172.2.1.2/24 |
Configuration procedure
Configure UPE 1:
# Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP to establish LDP LSPs.
<UPE1> system-view [UPE1] interface loopback 0 [UPE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [UPE1-LoopBack0] quit [UPE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [UPE1] mpls ldp [UPE1-ldp] quit [UPE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/3 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] ip address 172.1.1.1 24 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] mpls enable [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] mpls ldp enable [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] quit
# Configure the IGP protocol (OSPF, in this example).
[UPE1] ospf [UPE1-ospf-1] area 0 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [UPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [UPE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2, allowing CE 1 and CE 2 to access UPE 1.
[UPE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 100:1 [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [UPE1] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 100:2 [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 100:2 both [UPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit [UPE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [UPE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip binding vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip address 10.4.1.2 24 [UPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship with SPE 1.
[UPE1] bgp 100 [UPE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [UPE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [UPE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [UPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [UPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship with CE 1.
[UPE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65410 [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast [UPE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.2.1.1 enable [UPE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship with CE 2.
[UPE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn2] peer 10.4.1.1 as-number 65420 [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn2] address-family ipv4 unicast [UPE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn2] peer 10.4.1.1 enable [UPE1-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn2] quit [UPE1-bgp-default-vpn2] quit [UPE1-bgp-default] quit
Configure CE 1.
<CE1> system-view [CE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 [CE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [CE1] bgp 65410 [CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 [CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast [CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.2.1.2 enable [CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct [CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit [CE1-bgp-default] quit
Configure CE 2.
<CE2> system-view [CE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 [CE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [CE2] bgp 65420 [CE2-bgp-default] peer 10.4.1.2 as-number 100 [CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast [CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.4.1.2 enable [CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct [CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit [CE2-bgp-default] quit
Configure UPE 2:
# Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP to establish LDP LSPs.
<UPE2> system-view [UPE2] interface loopback 0 [UPE2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.9 32 [UPE2-LoopBack0] quit [UPE2] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 [UPE2] mpls ldp [UPE2-ldp] quit [UPE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 172.2.1.1 24 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls enable [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls ldp enable [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure the IGP protocol (OSPF, in this example).
[UPE2] ospf [UPE2-ospf-1] area 0 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 [UPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [UPE2-ospf-1] quit
# Configure VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2, allowing CE 3 and CE 4 to access UPE 2.
[UPE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 300:1 [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [UPE2] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 400:2 [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 100:2 both [UPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit [UPE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] quit [UPE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/3 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] ip binding vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] ip address 10.3.1.2 24 [UPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] quit
# Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship with SPE 2.
[UPE2] bgp 100 [UPE2-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [UPE2-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [UPE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [UPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [UPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship with CE 3.
[UPE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65430 [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn1] address-family ipv4 unicast [UPE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 enable [UPE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn1] quit [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit
# Establish an EBGP peer relationship with CE 4.
[UPE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn2] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 65440 [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn2] address-family ipv4 unicast [UPE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn2] peer 10.3.1.1 enable [UPE2-bgp-default-ipv4-vpn2] quit [UPE2-bgp-default-vpn2] quit [UPE2-bgp-default] quit
Configure CE 3.
<CE3> system-view [CE3] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE3-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [CE3-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [CE3] bgp 65430 [CE3-bgp-default] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [CE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast [CE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.1.1.2 enable [CE3-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct [CE3-bgp-default-ipv4] quit [CE3-bgp-default] quit
Configure CE 4.
<CE4> system-view [CE4] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [CE4-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 [CE4-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [CE4] bgp 65440 [CE4-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 100 [CE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast [CE4-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.2 enable [CE4-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct [CE4-bgp-default-ipv4] quit [CE4-bgp-default] quit
Configure SPE 1:
# Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP to establish LDP LSPs.
<SPE1> system-view [SPE1] interface loopback 0 [SPE1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [SPE1-LoopBack0] quit [SPE1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [SPE1] mpls ldp [SPE1-ldp] quit [SPE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 172.1.1.2 24 [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls enable [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls ldp enable [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [SPE1] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip address 180.1.1.1 24 [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] mpls enable [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] mpls ldp enable [SPE1-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] quit
# Configure the IGP protocol, OSPF, in this example.
[SPE1] ospf [SPE1-ospf-1] area 0 [SPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [SPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 180.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [SPE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2.
[SPE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 500:1 [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [SPE1] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 700:1 [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 100:2 both [SPE1-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit
# Establish MP-IBGP peer relationships with SPE 2 and UPE 1, and specify UPE 1 as a UPE.
[SPE1] bgp 100 [SPE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [SPE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [SPE1-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [SPE1-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [SPE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 upe [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 next-hop-local [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
# Create BGP-VPN instances for VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2, so the VPNv4 routes learned according to the RT attributes can be added into the BGP routing tables of the corresponding VPN instances.
[SPE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [SPE1-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [SPE1-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [SPE1-bgp-default-vpn2] quit [SPE1-bgp-default] quit
# Advertise to UPE 1 the routes permitted by a routing policy (the routes of CE 3).
[SPE1] ip prefix-list hope index 10 permit 10.1.1.1 24 [SPE1] route-policy hope permit node 0 [SPE1-route-policy-hope-0] if-match ip address prefix-list hope [SPE1-route-policy-hope-0] quit [SPE1] bgp 100 [SPE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [SPE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 upe route-policy hope export
Configure SPE 2:
# Configure basic MPLS and MPLS LDP to establish LDP LSPs.
<SPE2> system-view [SPE2] interface loopback 0 [SPE2-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [SPE2-LoopBack0] quit [SPE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [SPE2] mpls ldp [SPE2-ldp] quit [SPE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] ip address 180.1.1.2 24 [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls enable [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] mpls ldp enable [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit [SPE2] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip address 172.2.1.2 24 [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] mpls enable [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] mpls ldp enable [SPE2-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] quit
# Configure the IGP protocol, OSPF, in this example.
[SPE2] ospf [SPE2-ospf-1] area 0 [SPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 [SPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 172.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 180.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [SPE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [SPE2-ospf-1] quit
# Configure VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2.
[SPE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 600:1 [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] vpn-target 100:1 both [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [SPE2] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] route-distinguisher 800:1 [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] vpn-target 100:2 both [SPE2-vpn-instance-vpn2] quit
# Establish MP-IBGP peer relationships with SPE 1 and UPE 2, and specify UPE 2 as a UPE.
[SPE2] bgp 100 [SPE2-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 [SPE2-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [SPE2-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [SPE2-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 0 [SPE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.9 enable [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.9 upe [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.9 next-hop-local [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
# Create BGP-VPN instances for VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2, so the VPNv4 routes learned according to the RT attributes can be added into the BGP routing tables of the corresponding VPN instances.
[SPE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [SPE2-bgp-default-vpn1] quit [SPE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance vpn2 [SPE2-bgp-default-vpn2] quit [SPE2-bgp-default] quit
# Advertise to UPE 2 the routes permitted by a routing policy (the routes of CE 1).
[SPE2] ip prefix-list hope index 10 permit 10.2.1.1 24 [SPE2] route-policy hope permit node 0 [SPE2-route-policy-hope-0] if-match ip address prefix-list hope [SPE2-route-policy-hope-0] quit [SPE2] bgp 100 [SPE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4 [SPE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.9 upe route-policy hope export
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that CE 1 and CE3 can learn each other's interface routes and can ping each other. CE 2 and CE 4 cannot learn each other's interface routes and cannot ping each other. (Details not shown.)