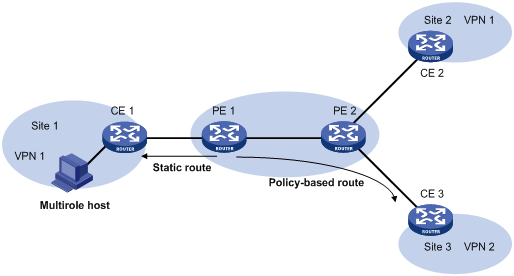
Multirole host
Typically, hosts in the same VPN can communicate with each other, and those in different VPNs cannot. However, a host or server in a site might need to access VPNs in addition to the VPN to which the host or server belongs. To simplify configuration, you can use the multirole host feature.
The multirole host feature enables a PE to use PBR to provide multiple VPN access for a host or server. The host or server is called a multirole host.
Figure 61: Network diagram
As shown in Figure 61, the multirole host in site 1 needs to access both VPN 1 and VPN 2. Other hosts in site 1 only need to access VPN 1. To configure the multirole host feature, configure PE 1 as follows:
Create VPN instances vpn1 and vpn2 for VPN 1 and VPN 2, respectively.
Associate VPN instance vpn1 with the interface connected to CE 1.
Configure PBR to route packets from CE 1 first by the routing table of the associated VPN instance (vpn1). Then, if no matching route is found, route the packets according to the routing table of VPN instance vpn2. This configuration ensures that packets from Site 1 can be forwarded in both VPN 1 and VPN 2.
Configure a static route for VPN instance vpn2 to reach the multirole host. Specify the next hop of the route as the IP address of CE 1 and specify the VPN instance to which the next hop belongs as VPN 1. This configuration ensures that packets from VPN 2 can be routed to the multirole host.
Configure static routes for all VPN instances that the multirole host needs to access, except the associated VPN instance.
![[IMPORTANT: ]](images/important.png) | IMPORTANT: IP addresses in all VPNs that the multirole host can access must not overlap. | |