Carrier's carrier
If a customer of an MPLS L3VPN service provider is also a service provider:
The MPLS L3VPN service provider is called the provider carrier or the Level 1 carrier.
The customer is called the customer carrier or the Level 2 carrier.
This networking model is referred to as carrier's carrier.
The PEs of the Level 2 carrier directly exchange customer networks over a BGP session. The Level 1 carrier only learns the backbone networks of the Level 2 carrier, without learning customer networks.
For packets between customer networks to travel through the Level 1 carrier, the PE of the Level 1 carrier and the CE of the Level 2 carrier must assign labels to the backbone networks of the Level 2 carrier. The CE of the Level 2 carrier is a PE within the Level 2 carrier network.
Follow these guidelines to assign labels:
If the PE and the CE are in the same AS, you must configure IGP and LDP between them. If they are in different ASs, you must configure MP-EBGP to assign labels to IPv4 unicast routes exchanged between them.
You must enable MPLS on the CE of the Level 2 carrier regardless of whether the PE and CE are in the same AS.
A Level 2 carrier can be an ordinary ISP or an MPLS L3VPN service provider.
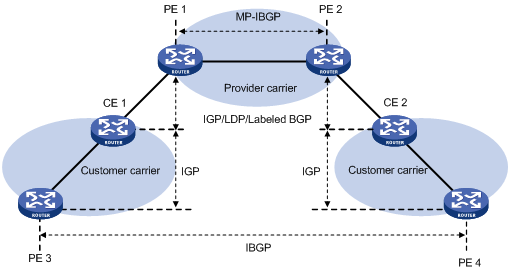
As shown in Figure 58, when the customer carrier is an ordinary ISP, its PEs and CEs run IGP to communicate with each other. The PEs do not need to run MPLS. PE 3 and PE 4 exchange customer network routes (IPv4 unicast routes) through an IBGP session.
Figure 58: Scenario where the Level 2 carrier is an ISP
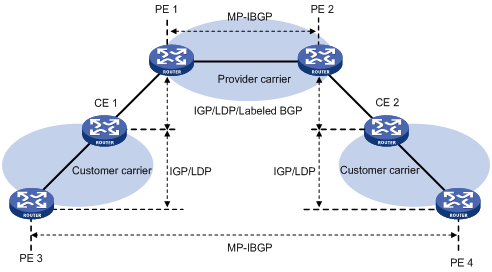
As shown in Figure 59, when the customer carrier is an MPLS L3VPN service provider, its PEs and CEs must run IGP and LDP to communicate with each other. PE 3 and PE 4 exchange customer network routes (VPN-IPv4 routes) through an MP-IBGP session.
Figure 59: Scenario where the Level 2 carrier is an MPLS L3VPN service provider
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: As a best practice, establish equal cost LSPs between the Level 1 carrier and the Level 2 carrier if equal cost routes exist between them. | |