Configuration example for connecting a LAN to the Internet through an ADSL modem
Network requirements
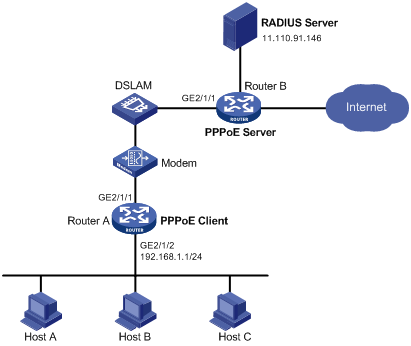
As shown in Figure 22:
Router A provides Internet access for Host A, Host B, and Host C. It connects to the DSLAM through an ADSL modem and a permanent PPPoE session.
The username and password of the ADSL account are user1 and 123456.
Router A operates as a PPPoE client, and it allows the hosts in the LAN to access the Internet without PPPoE client software.
Router B operates as the PPPoE server. It performs RADIUS authentication and accounting.
Figure 22: Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Configure Router A as a PPPoE client:
# Enable bundle DDR on Dialer 1.
<RouterA> system-view [RouterA] interface dialer 1 [RouterA-Dialer1] dialer bundle enable
# Configure Dialer 1 to obtain an IP address through PPP negotiation.
[RouterA-Dialer1] ip address ppp-negotiate
# Configure the PPPoE session to operate in permanent mode.
[RouterA-Dialer1] dialer timer idle 0
# Configure the PAP username and password.
[RouterA-Dialer1] ppp pap local-user user1 password simple 123456 [RouterA-Dialer1] quit
# Configure a PPPoE session.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] pppoe-client dial-bundle-number 1 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure an IP address for the LAN interface.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/2 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 [RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/1/2] quit
# Configure a default route.
[RouterA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 dialer 1
If the hosts in the LAN use private addresses, configure NAT on Router A. For more information about NAT, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Configure Router B as the PPPoE server:
# Configure Virtual-Template 1 to use PAP for authentication and use a PPP address pool to assign IP addresses.
<RouterB> system-view [RouterB] interface virtual-template 1 [RouterB-Virtual-Template1] ppp authentication-mode pap domain system [RouterB-Virtual-Template1] remote address pool 1 [RouterB-Virtual-Template1] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 [RouterB-Virtual-Template1] quit
# Configure a local PPP address pool that contains nine assignable IP addresses.
[RouterB] ip pool 1 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.10
# Enable the PPPoE server on GigabitEthernet 2/1/1.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/1 [RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] pppoe-server bind virtual-template 1 [RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/1/1] quit
# Configure the default ISP domain (system) to use the RADIUS scheme for authentication, authorization, and accounting.
[RouterB] domain system [RouterB-isp-system] authentication ppp radius-scheme rs [RouterB-isp-system] authorization ppp radius-scheme rs [RouterB-isp-system] accounting ppp radius-scheme rs [RouterB-isp-system] quit
# Configure a RADIUS scheme, and assign an IP address and port number for the RADIUS server.
[RouterB] radius scheme rs [RouterB-radius-rs] primary authentication 11.110.91.146 1812 [RouterB-radius-rs] primary accounting 11.110.91.146 1813
# Set the shared keys for secure communication with the RADIUS server to expert in plain text.
[RouterB-radius-rs] key authentication simple expert [RouterB-radius-rs] key accounting simple expert [RouterB-radius-rs] quit
Configure the RADIUS server:
# Configure the authentication and accounting passwords as expert.
# Add a PPPoE user with username user1 and password 123456.
For more information about RADIUS, see Security Configuration Guide.
Verifying the configuration
# Display summary information for the PPPoE session between Router A and Router B.
[RouterA] display pppoe-client session summary Bundle ID Interface VA RemoteMAC LocalMAC State 1 1 GE2/1/1 VA0 0001-0000-0001 00e0-1500-4100 SESSION
Host A, Host B, and Host C can thus access the Internet. For example, they can browse a web page through IE.