Overview
EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security) is one of the preferred authentication methods in enterprise business. EAP-TLS provides secured certificate-based mutual authentication of the client and the network.
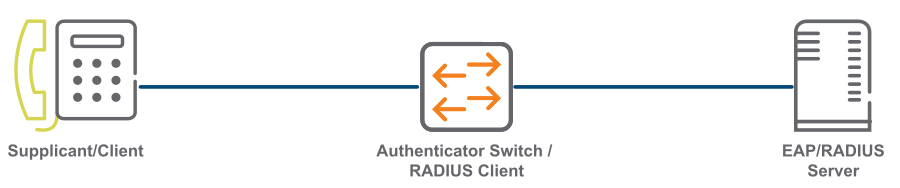
The Supplicant, or client is a device requesting access to the network.
Authenticator, or switch is a network device providing link between the supplicant and a RADIUS server. It can allow or block network traffic between the supplicant and server.
RADIUS, or EAP server validates and authenticates the client.
Currently, EAP-TLS support on Aruba switch allows a client or a EAP/RADIUS server to exchange data packet of standard MTU size. When jumbo is enabled on a switch, the client and the EAP server can send data packets up to MTU size of 9k bytes. But, the maximum MTU size allowed between the switch and the RADIUS server is 3k bytes. RADIUS server cannot process any inbound packet greater than 3k bytes, thus the switch fails to complete the EAP authentication process.
Now, Aruba switch supports an internal EAP fragmentation for EAP-TLS to exchange the RADIUS packets between a client and a RADIUS server. With this enhancement, you can enable jumbo and EAP-TLS authentication together on switch. This feature supports high size chain certificates on both Windows and Linux clients.
The IP fragmentation must be enabled between the switch and the RADIUS server. The IP MTU size must be set appropriately to handle the RADIUS packets. The switch performs the following functions for a successful exchange of RADIUS packets between the client and the RADIUS server:
Fragments the EAP Request data during a server-client key exchange.
Fragments the EAP Response data during a supplicant-client key exchange.
Reassembles the fragmented EAP Request data.
Reassembles the fragmented EAP Response data.