Event Log entries
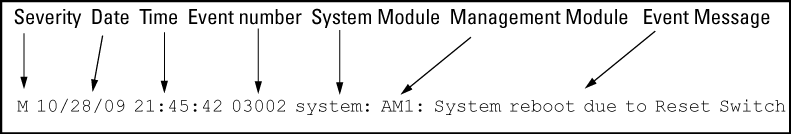
As shown in Figure 40: Format of an event log entry, each Event Log entry is composed of six or seven fields, depending on whether numbering is turned on or not:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
Severity |
One of the following codes (from highest to lowest severity): M—(major) indicates that a fatal switch error has occurred. E—(error) indicates that an error condition occurred on the switch. W—(warning) indicates that a switch service has behaved unexpectedly.I—(information) provides information on normal switch operation. D—(debug) is reserved for internal diagnostic information. |
Date |
The date in the format mm/dd/yy when an entry is recorded in the log. |
Time |
The time in the format hh:mm:ss when an entry is recorded in the log. |
Event number |
The number assigned to an event. You can turn event numbering on and off with the
|
System module |
The internal module (such as "ports:" for port manager) that generated a log entry. If VLANs are configured, a VLAN name also appears for an event that is specific to an individual VLAN. |
Event message |
A brief description of the operating event. |
System module |
Description |
Documented in Switch hardware/software guide |
|---|---|---|
802.1x |
802.1X authentication: Provides access control on a per-client or per-port basis:
|
Access Security Guide |
addrmgr |
Address Table Manager: Manages MAC addresses that the switch has learned and are stored in the switch's address table. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
auth |
Authorization: A connected client must receive authorization through web, AMC, RADIUS-based, TACACS+-based, or 802.1X authentication before it can send traffic to the switch. |
Access Security Guide |
cdp |
Cisco Discovery Protocol: Supports reading CDP packets received from neighbor devices, enabling a switch to learn about adjacent CDP devices. HPE does not support the transmission of CDP packets to neighbor devices. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
console |
Console interface used to monitor switch and port status, reconfigure the switch, and read the event log through an in-band Telnet or out-of-band connection. |
Installation and Getting Started Guide |
cos |
Class of Service (CoS): Provides priority handling of packets traversing the switch, based on the IEEE 802.1p priority carried by each packet.CoS messages also include QoS events. The QoS feature classifies and prioritizes traffic throughout a network, establishing an end-to-end traffic priority policy to manage available bandwidth and improve throughput of important data. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
dhcp |
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server configuration: Switch is automatically configured from a DHCP (Bootp) server, including IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, Timep Server address, and TFTP server address. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
dhcp v6c |
DHCP for IPv6 prefix assignment |
IPv6 Configuration Guide |
dhcpr |
DHCP relay: Forwards client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP network server. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
download |
Download operation for copying a software version or files to the switch. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
dma |
Direct Access Memory (DMA): Transmits and receives packets between the CPU and the switch. |
— |
fault |
Fault Detection facility, including response policy and the sensitivity level at which a network problem should generate an alert. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
ffi |
Find, Fix, and Inform: Event or alert log messages indicating a possible topology loop that causes excessive network activity and results in the network running slow. FFI messages include events on transceiver connections with other network devices. |
Installation and Getting Started Guide Management and Configuration Guide |
garp |
Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP), defined in the IEEE 802.1D-1998 standard. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
gvrp |
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP): Manages dynamic 802.1Q VLAN operations, in which the switch creates temporary VLAN membership on a port to provide a link to another port in the same VLAN on another device. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
hpesp |
Management module that maintains communication between switch ports. |
Installation and Getting Started Guide |
igmp |
Internet Group Management Protocol: Reduces unnecessary bandwidth usage for multicast traffic transmitted from multimedia applications on a per-port basis. |
Multicast and Routing Guide |
ip |
IP addressing: Configures the switch with an IP address and subnet mask to communicate on the network and support remote management access; configures multiple IP addresses on a VLAN; enables IP routing on the switch. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
iplock |
IP Lockdown: Prevents IP source address spoofing on a per-port and per-VLAN basis by forwarding only the IP packets in VLAN traffic that contain a known source IP address and MAC address binding for the port. |
Access Security Guide |
ipx |
Novell Netware protocol filtering: On the basis of protocol type, the switch can forward or drop traffic to a specific set of destination ports on the switch. |
Access Security Guide |
lacp |
LACP trunks: The switch can either automatically establish an 802.3ad-compliant trunk group or provide a manually configured, static LACP trunk. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
ldbal |
Load balancing in LACP port trunks or 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree protocol (MSTP) that uses VLANs in a network to improve network resource utilization and maintain a loop-free environment.Load-balancing messages also include switch meshing events. The switch meshing feature provides redundant links, improved bandwidth use, and support for different port types and speeds. |
Management and Configuration Guide Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
lldp |
Link-Layer Discovery Protocol: Supports transmitting LLDP packets to neighbor devices and reading LLDP packets received from neighbor devices, enabling a switch to advertise itself to adjacent devices and to learn about adjacent LLDP devices. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
macauth |
Web and MAC authentication: Port-based security employed on the network edge to protect private networks and the switch itself from unauthorized access using one of the following interfaces:
|
Access Security Guide |
maclock |
MAC lockdown and MAC lockout
|
Access Security Guide |
mgr |
Windows-based network management solutions for managing and monitoring performance of HPE switches. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
netinet |
Network Internet: Monitors the creation of a route or an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entry and sends a log message in case of failure. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
pagp |
Ports Aggregation Protocol (PAgP): Obsolete. Replaced by LACP (802.3ad). |
— |
ports |
Port status and port configuration features, including mode (speed and duplex), flow control, broadcast limit, jumbo packets, and security settings. Port messages include events on POE operation and transceiver connections with other network devices. |
Installation and Getting Started Guide Management and Configuration Guide Access Security Guide |
radius |
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication and accounting: A network server is used to authenticate user-connection requests on the switch and collect accounting information to track network resource usage. |
Access Security Guide |
snmp |
Simple Network Management Protocol: Allows you to manage the switch from a network management station, including support for security features, event reporting, flow sampling, and standard MIBs. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
sntp |
Simple Network Time Protocol: Synchronizes and ensures a uniform time among interoperating devices. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
ssh |
Secure Shell version 2 (SSHv2): Provides remote access to management functions on a switch via encrypted paths between the switch and management station clients capable of SSH operation. SSH messages also include events from the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) feature. SFTP provides a secure alternative to TFTP for transferring sensitive information, such as switch configuration files, to and from the switch in an SSH session. |
Access Security Guide |
ssl |
Secure Socket Layer Version 3 (SSLv3), including Transport Layer Security (TLSv1) support: Provides remote web access to a switch via encrypted paths between the switch and management station clients capable of SSL/TLS operation. |
Access Security Guide |
stack |
Stack management: Uses a single IP address and standard network cabling to manage a group (up to 16) of switches in the same IP subnet (broadcast domain), resulting in a reduced number of IP addresses and simplified management of small workgroups for scaling your network to handle increased bandwidth demand. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
stp |
Multiple-instance spanning tree protocol/MSTP (802.1s): Ensures that only one active path exists between any two nodes in a group of VLANs in the network. MSTP operation is designed to avoid loops and broadcast storms of duplicate messages that can bring down the network. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
system |
Switch management, including system configuration, switch bootup, activation of boot ROM image, memory buffers, traffic and security filters. System messages also include events from management interfaces (menu and CLI) used to reconfigure the switch and monitor switch status and performance. |
Management and Configuration Guide Access Security Guide |
tacacs |
TACACS+ authentication: A central server is used to control access to the switches (and other TACACS-aware devices) in the network through a switch's console port (local access) or Telnet (remote access). |
Access Security Guide |
tcp |
Transmission Control Protocol: A transport protocol that runs on IP and is used to set up connections. |
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
telnet |
Session established on the switch from a remote device through the Telnet virtual terminal protocol. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
tftp |
Trivial File Transfer Protocol: Supports the download of files to the switch from a TFTP network server. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
timep |
Time Protocol: Synchronizes and ensures a uniform time among interoperating devices. |
Management and Configuration Guide |
update |
Updates (TFTP or serial) to switch software and updates to running-config and start-up config files |
Management and Configuration Guide |
vlan |
Static 802.1Q VLAN operations, including port-and protocol-based configurations that group users by logical function instead of physical location
|
Advanced Traffic Management Guide |
xmodem |
Xmodem: Binary transfer feature that supports the download of software files from a PC or UNIX workstation. |
Management and Configuration Guide |