Duplicate MAC addresses across VLANs
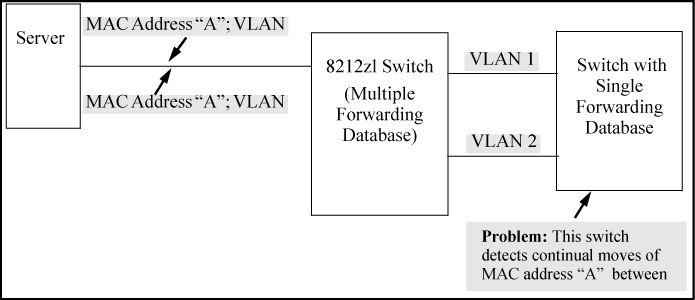
The switches operate with multiple forwarding databases. Thus, duplicate MAC addresses occurring on different VLANs can appear where a device having one MAC address is a member of more than one 802.1Q VLAN, and the switch port to which the device is linked is using VLANs (instead of MSTP or trunking) to establish redundant links to another switch. If the other device sends traffic over multiple VLANs, its MAC address consistently appears in multiple VLANs on the switch port to which it is linked.
Be aware that attempting to create redundant paths through the use of VLANs causes problems with some switches. One symptom is that a duplicate MAC address appears in the Port Address Table of one port and then later appears on another port. While the switches have multiple forwarding databases and thus do not have this problem, some switches with a single forwarding database for all VLANs may produce the impression that a connected device is moving among ports because packets with the same MAC address but different VLANs are received on different ports. You can avoid this problem by creating redundant paths using port trunks or spanning tree.