Using GVRP
When GVRP is enabled on a switch, the VID for any static VLAN configured on the switch is advertised, using BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units), out all ports regardless of whether a port is up or assigned to any particular VLAN. A GVRP-aware port on another device that receives the advertisements over a link can dynamically join the advertised VLAN.
A dynamic VLAN (that is, a VLAN learned through GVRP) is tagged on the port on which it was learned. Also, a GVRP-enabled port can forward an advertisement for a VLAN it learned about from other ports on the same switch (internal source), but the forwarding port will not itself join that VLAN until an advertisement for that VLAN is received through a link from another device (external source) on that specific port.
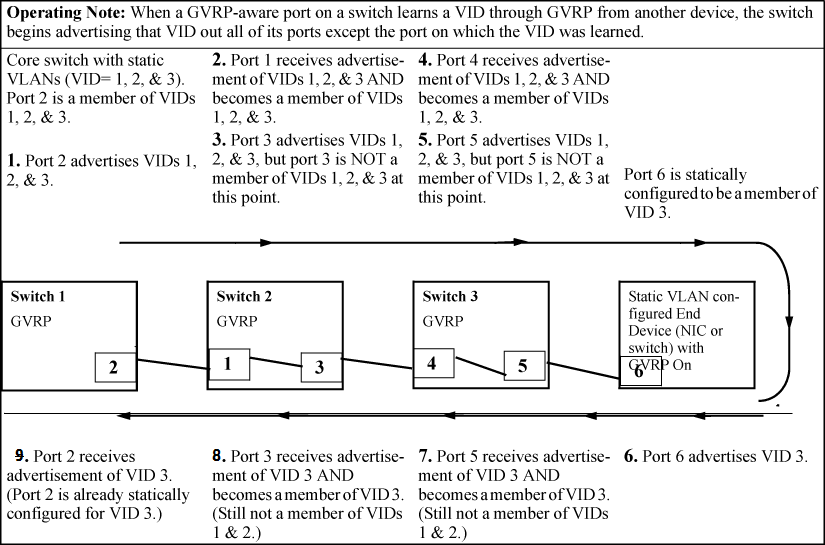
If a static VLAN is configured on at least one port of a switch, and that port has established a link with another device, then all other ports of that switch will send advertisements for that VLAN.
A port can learn of a dynamic VLAN through devices that are not aware of GVRP. VLANs must be disabled in GVRP-unaware devices to allow tagged packets to pass through.