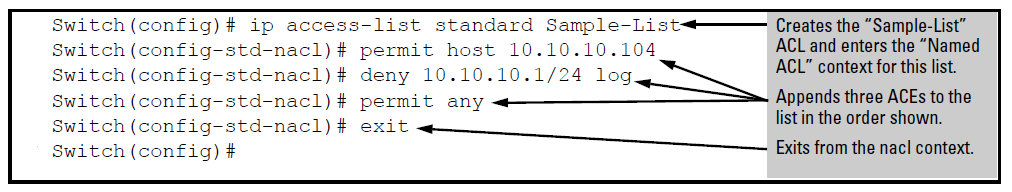
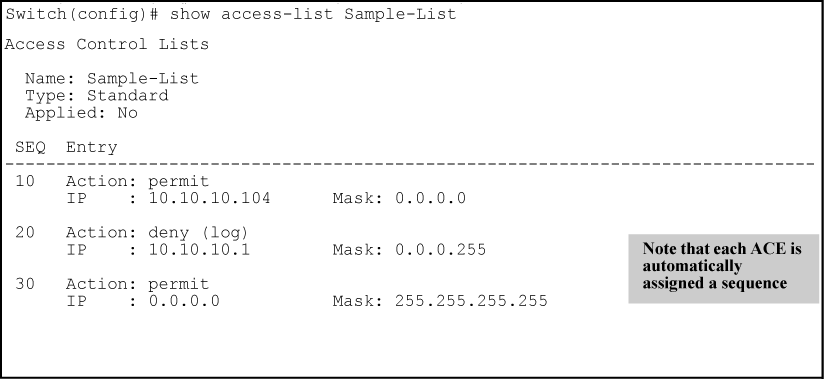
Configuring ACEs in a named, standard ACL
Configuring ACEs is done after using the
ip access-list standard <name-str> command to enter the "Named ACL" (
nacl) context of an access list.
Syntax
{<deny | permit>}
{<any | host <SA> | SA <mask | SA/ mask-length>>} [log]
Executing this command appends the ACE to the end of the list of ACEs in the current ACL. In the default ACL configuration, ACEs are automatically assigned consecutive sequence numbers in increments of 10 and can be renumbered using resequence (See Resequencing the ACEs in an ACL.)
To insert a new ACE between two existing ACEs, precede
deny or
permit with an appropriate sequence number. See
Inserting an ACE in an existing ACL.
{<deny | permit>}
For named ACLs, used in the "Named ACL" (
nacl) context to configure an ACE. Specifies whether the ACE denies or permits a packet matching the criteria in the ACE, as described below.
{<any | host <SA> | SA <mask | SA/ mask-length>>}
Defines the source IPv4 address (SA) a packet must carry for a match with the ACE.
anyAllows IPv4 packets from any SA.
-
host <SA>Specifies only packets having <SA> as the source. Use this criterion when you want to match the IPv4 packets from a single source address.
SA <mask>or
SA /mask–lengthSpecifies packets received from either a subnet or a group of IPv4 addresses. The mask format can be in either dotted-decimal format or CIDR format (number of significant bits). See How an ACE uses a mask to screen packets for matches.-
Mask ApplicationThe mask is applied to the IPv4 address in the ACE to define which bits in a packet's SA must exactly match the SA configured in the ACE and which bits need not match. For example:
10.10.10.1/24and10.10.10.1 0.0.0.255both define any address in the range of 10.10.10.(1 - 255).NOTE:Specifying a group of contiguous addresses may require more than one ACE. For more on how masks operate, see How an ACE uses a mask to screen packets for matches.
[log]This option generates an ACL log message if:-
The action is deny.
-
There is a match.
-
ACL logging is enabled on the switch. See Enabling ACL logging on the switch for more details.
-
Use the debug command to direct ACL logging output to the current console session and to a Syslog server. Note that you must also use the
logging <ip-addr>command to specify the addresses of Syslog servers to which you want log messages sent. See also Enabling ACL logging on the switch.
-
Example
This example creates an ACL that:
-
permits IPv4 traffic from a host with the address of 10.10.10.104
-
creates another ACE that blocks all other IPv4 traffic from the same subnet
-
allows all other IPv4 traffic.